
Joao Luis Silva Damas developed the tools used in this experiment.
Following the publication of RFC 7872 in 2016, a number of research teams have been looking at the nature of network and host behaviours in discarding IPv6 packets with various extension headers (EH). The findings reported in RFC 7872 were a significant level of packet loss (‘significant’ being above 10% in all cases) for IPv6 packets that contained extension headers that carried Destination Options (DST), Hop-by-Hop Options (HBH) and Fragmentation Controls (Frag).
| DST | HBH | Frag | |
| World IPv6 Day data set | 11.88% | 40.70% | 30.51% |
| Alexa Top 1M | 10.91% | 45.45% | 28.26% |
Further work has varied the contexts in which the test for support of IPv6 extension headers has been performed, and the reported results of these measurement exercises have varied considerably. Recent work has attempted to reconcile these differences, such as the work presented during the March 2023 IEPG by the University of Aberdeen’s Ana Custura and Gorry Fairhurst on IPv6 EH measurement.
There is little doubt that these kinds of measurements are challenging. We are looking at the characteristics of various end-to-end paths through the public Internet, and there is a considerable diversity of paths. Looking at the public Internet as a largely client/server network then we have client-to-client, server-to-server, client-to-server, and server-to-client to consider (Figure 1).
What is the likely scenario of using HBH EH? Is it used in packets that originated at the edge and are sent toward servers (this is the scenario that was measured for RFC 7872)? Or is this a server-side function, and likely to be sent from servers to clients? Or is this useful in the server-to-server environment? There are many different server environments of course, and measurements conducted using one server environment cannot readily be generalized to all servers.
This is a report on some further investigation of the IPv6 EH drop behaviour, extending the APNIC Labs report published in October 2022 using the APNIC Labs edge-based measurement methodology.
In this work, we’ve compared measurements from the existing APNIC Labs measurement infrastructure with measurements from a server located at the facilities at the University of Aberdeen. The objective of these measurements was to attempt to identify where IPv6 packets with EH extensions were being dropped, and in particular to determine whether the Linode service operated by AKAMAI, was responsible for the extremely high EH drop rate (recorded at 99.89% drop rate in June 2023) as seen in the APNIC Labs measurements.
Edge-based measurement
APNIC Labs measurement approach uses a server-to-edge measurement approach. Edge hosts performing the measurement are recruited through an online advertisement campaign. These edge hosts execute an HTML5 script that has been packaged into the advertisement, and the script directs the host to perform a set of URL fetches. These fetches all use a server collection operated by APNIC.
Each measurement server is capable of various behaviours, and the edge host then reports back on the success or failure to load each of the URLs that it was tasked to perform. The servers perform logging of all DNS and HTTPS transactions, as well as performing a full packet header capture of all traffic.
The servers are virtual hosts, located in Europe, North America, South America, and Asia. The majority of the servers are implemented using a Linode virtual host service, although Amazon AWS instances are also used, as well as one dedicated hardware platform.
In this measurement of support for IPv6 extension headers, the edge hosts open an IPv6 TCP session with the server where the server sends outbound TCP packets back to the client where the packets’ IPv6 header has an EH.
To briefly recap the technical details of this measurement, we use an active proxy in the end-to-end HTTPS session, and for all TCP packets larger than 512 bytes in size we add an EH into the outgoing packet stream. We use three different types of EHs:
- Fragmentation header, where the initial packet is set to a size of 1,200, 1,208, 1,216, and so on through to 1,416 octets, with the initial fragment size randomly selected from this set.
- Destination Option (DST) header, where the option used is PadN with using padding sizes of 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128 bytes.
- Hop-By-Hop Option header, where the option used is PadN with padding sizes of 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128 bytes.
The result for IPv6 packets with DST headers is a drop rate of some 30% when the DST option size is 64 bytes or less, and some 55% when the option is 128 bytes. This drop rate was 90% until early April 2023, when it dropped to 55%. No root cause for the change in the results for the DST option measurement has been identified as yet.
The result for the packet rate for IPv6 packets with HBH headers is a consistent drop rate of 99.89%. There has been some speculation that this observed packet discard behaviour for packets with HBH headers is happening as the packet is leaving the Linode hosting network. In other words, this HBH drop measurement might be impacted by a local behaviour in Linode’s packet-switching environment.
To further investigate this behaviour, we have set up a parallel experiment using a virtual host located on a server located at the University of Aberdeen, hosted within the JANET UK Academic and Research Network. A separate advertising campaign has been used to seed this measurement, with the campaign settings limiting the advertisement to presentations within the UK locale. Our expectation from this measurement is that if the Linode-hosted environment is discarding packets with HBH headers, and if this Linode behaviour is anomalous to some extent when compared to other networks, then the observed drop rate for the University of Aberdeen-hosted server would be substantially lower than that seen from the Linode servers.
Results
University of Aberdeen server measurements
The experiments used the IPv6 HBH EHs with a single field of a padding option. The size of the padding option was varied across the range of 8 bytes to 128 bytes, where each measurement instance randomly selected a padding size to use. The result of this experiment was a packet drop rate of 99.04% for HBH IPv6 packets. The first impression is that this result is not significantly different from the APNIC Labs result of a drop rate of 99.89% and is not conclusive in terms of determining whether the Linode service environment is dropping outbound HBH packets or not. However, further examination of this data can shed some further light on this question.
| HBH Option Size | Total | Drop | Drop rate |
| 8 | 67,256 | 66,079 | 98.25% |
| 16 | 67,560 | 66,402 | 98.29% |
| 32 | 67,343 | 66,140 | 98.21% |
| 64 | 101,344 | 101,322 | 99.98% |
| 128 | 67,239 | 67,230 | 99.99% |
| Total | 370,742 | 367,173 | 99.04% |
As shown in Table 2, there is some small variation in the observed drop rate of the University of Aberdeen measurements across the various option sizes, varying between 98.25% for smaller HBH EH options, while the larger sizes have a drop rate of 99.98%. There appear to be two behaviours here, one for EH options of size 32 bytes or less and one for EH options of 64 bytes or greater.
However, a more significant indication of where this packet drop is occurring can be found when we look at the host network for each of the tested endpoints. The breakdown of these measurements by originating Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the end user is shown in Table 3. This table lists the 10 ASNs in the UK that have the largest number of sampled users. In Table 3, the HBH padding option sizes of 8, 16 and 32 bytes are grouped together as small and 64 and 128 bytes are grouped together as large.
| ASN | Samples | Small | Drops | Rate | Large | Drops | Rate | AS name |
| AS2856 | 205,357 | 111,767 | 111,742 | 99.98% | 93,590 | 93,569 | 99.98% | BTnet UK Regional network |
| AS206067 | 47,379 | 25,991 | 25,991 | 100.00% | 21,388 | 21,387 | 100.00% | H3GUK |
| AS5607 | 37,436 | 20,284 | 20,277 | 99.97% | 17,152 | 17,150 | 99.99% | BSKYB-BROADBAND-AS |
| AS201838 | 24,819 | 13,664 | 13,664 | 100.00% | 11,155 | 11,155 | 100.00% | ASN-AS |
| AS12576 | 12,733 | 7,010 | 7,007 | 99.96% | 5,723 | 5,721 | 99.97% | EE Ltd |
| AS56478 | 6,907 | 3,779 | 3,779 | 100.00% | 3,128 | 3,127 | 99.97% | BCUBE-AS |
| AS13335 | 5,366 | 2,863 | 376 | 13.13% | 2,503 | 2,502 | 99.96% | CLOUDFLARENET |
| AS204731 | 4,837 | 2,664 | 2,664 | 100.00% | 2,173 | 2,173 | 100.00% | FIBRENEST |
| AS13037 | 4,219 | 2,316 | 2,316 | 100.00% | 1,903 | 1,901 | 99.89% | Zen Internet – UK |
| AS212655 | 3,455 | 1,892 | 1,580 | 83.51% | 1,563 | 1,563 | 100.00% | YOUFIBRE |
Only two ASNs have a less than comprehensive drop rate for HBH option packets, namely AS13335 (Cloudflare) and AS212655 (You Fibre)
APNIC Labs measurements using Linode servers
To compare these results from the University of Aberdeen server we’ll select only those tests where the measured endpoint is located in the UK, over the same time period as the tests using the University of Aberdeen server. This is shown in Table 4.
| HBH Option Size | Total | Drop | Drop rate |
| 8 | 149,065 | 149,063 | 100.00% |
| 16 | 147,964 | 147,961 | 100.00% |
| 32 | 149,367 | 149,361 | 100.00% |
| 64 | 279,690 | 279,678 | 100.00% |
| 128 | 149,088 | 179,083 | 100.00% |
| Total | 875,174 | 875,146 | 100.00% |
The drop rate for the 8-byte HBH header of 100.00%, and the differences between Tables 1 and 4, appear to provide a strong indication that the Linode server hosting environment is indeed dropping packets with HBH extension headers.
There is, however, one counter-indication in the Linode server data, namely the results for users located in Egypt (Table 5).
| HBH Option Size | Total | Drop | Drop rate |
| 8 | 11,746 | 9,609 | 81.81% |
| 16 | 11,875 | 11,252 | 94.75% |
| 32 | 11,657 | 9,519 | 81.66% |
| 64 | 22,024 | 17,807 | 80.85% |
| 128 | 11,671 | 9,411 | 80.64% |
| Total | 68,973 | 57,598 | 83.51% |
At least for IPv6 packets destined for tested users in Egypt, there is a far lower drop rate for packets with HBH extension headers, which appears to contradict the supposition that Linode is dropping all outbound HBH option packets.
IPv6 EH traceroute
To further investigate this behaviour, we constructed a variant of the traceroute tool that uses TCP SYN packets with configurable IPv6 EH options as probe packets and looks for matching ICMP6 time limit exceeded packets, thereby tracing the network path on an HBH basis.
The network path from the University of Aberdeen to Cloudflare exposed by this tool was the sequence of AS786 JANET (the UK Academic and Research Network), then LINX (the London Internet Exchange), and then AS13335 (Cloudflare). IPv6 packets with no EH, IPv6 packets with Destination EH and IPv6 packets with HBH EH all follow the same network path.
The network path from the University of Aberdeen to AS2856, the BTnet network, shows a direct connection between the JANET network and the BTnet network. When we use a HBH EH, the traceroute path stops at the egress point of the JANET network, indicating that the BTnet network ingress appears to be discarding HBH EH packets. This is consistent with the observed behaviour of the BTnet in Table 2, which shows an end-to-end drop rate of 99.98% for EH packets.
The inference from the results shown in Table 3 is that the local network infrastructure at the University of Aberdeen and the transit infrastructure within JANET support the passing of DST and HBH extension headers. Apart from Cloudflare and You Fibre, there are some issues with HBH EH support in reaching other UK networks.
It is unclear from this data set whether the packet discard is occurring on packet ingress into the target network, as is the case with BTnet, or within the network transit path such that a transit network is dropping HBH EH packets. To add some further clarity to this picture of the 10 largest customer networks in the UK, we used the EH traceroute tool to determine where the outbound EH packets were being dropped. The results of these probes are shown in Figure 2.
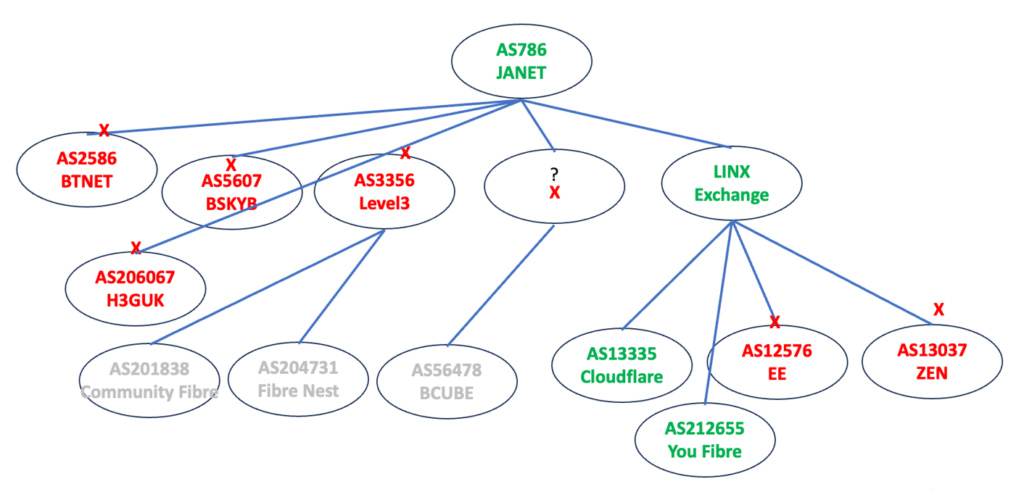
Both BTnet and H3GUK directly peer with JANET, and their ingress router drops incoming IPv6 EH packets with HBH headers. BSKYB is slightly different, in that the ingress router accepts their packet, but it is dropped at the next hop within the BSKYB network. Two networks, Community Fibre and Fibre Nest, use Level 3 as the transit network from JANET, and Level 3 is performing packet drop at the ingress router. The BCUBE sits behind a transit path that does not send ICMPv6 Time Limit Exceeded messages, so the transit operator is not identified in this process, but the HBH EH packet drop is happening in this unidentified transit network. The final four networks all interface to JANET via LINX, which passes IPv6 EH HBH packets. Both Cloudflare and You Fibre accept IPv6 EH HBH packets, while EE and ZEN discard such packets at their network ingress points.
What about the APNIC Labs results? The same traceroute tools show that the Akamai network, AS63949, (which hosts the Linode servers) is dropping IPv6 packets with HBH EH headers at the network’s egress router. This egress drop behaviour explains the behaviour of the HBH EH measurements as measured by APNIC Labs for all endpoints, with the single exception of Egypt.
This leaves us with an anomaly, in that the TCP-based test shows a drop rate of slightly over 80% for HBH EH packets destined for the Egyptian network provider ETLISAT-MISR, yet when we subsequently use the IPv6 EH traceroute tool to probe the paths, the packets are dropped at the network egress router in the same manner as all other such test packets. The EH traceroute tests use the same IPv6 destination addresses that passed the TCP session test. The difference here is that the traceroute tool uses TCP SYN packets, whereas the APNIC Labs tests add the HBH header onto packets of size greater than 512 bytes, which is after the TCP three-way handshake has completed. Therefore, the APNIC Labs test occurs only within the context of an established TCP session whereas the EH traceroute test is placed on the opening SYN packet. In any case, this does not adequately explain the singular results for this network in the APNIC Labs test.
Conclusions
We are now satisfied that the close to comprehensive EH drop observed in the APNIC Labs experiment is a result of a Linode environment setting that drops all such packets on egress from the Linode environment.
This behaviour is also observed in a number of other public Internet server environments, and from our tests it appears that the behaviour of the JANET network, the Cloudflare network, and the You Fibre network in forwarding such IPv6 packets are somewhat exceptional, and the typical network behaviour is to discard such packets.
Why would a service provider drop IPv6 packets with HBH EH settings? The issue here is that all IPv6 packets with HBH EH settings need to be passed to the router’s processor for every router that processes such a packet. In the context of the public Internet, this exposes the routing environment to a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack where a high-volume packet flow with HBH headers has the capacity to dominate the router’s packet processing queue thereby denying this processing capability to other packets and risks saturating the router’s processing capability.
Given that we’ve been unable to find a use case for HBH EH packets in production IPv6 networks then allowing routers to process such packets represents risk without any clearly identified benefit. Little wonder that most networks in the public Internet take the prudent course of action and drop such packets at the network’s ingress points.
What does all this imply about the viability of HBH EH in the public Internet? There may be end-to-end paths that allow the carriage of such packets, but there are also many networks that discard such packets. It’s an unreliable approach to implement host-to-network signalling at the IP level, and therefore best avoided in the public Internet.
The views expressed by the authors of this blog are their own and do not necessarily reflect the views of APNIC. Please note a Code of Conduct applies to this blog.
