
Time for another annual roundup from the world of IP addresses. Let’s see what has changed in the past 12 months in addressing the Internet and look at how IP address allocation information can inform us of the changing nature of the network itself.
Around 1992, the IETF gazed into its crystal ball and tried to understand how the Internet would evolve and what demands it would place on the addressing system as part of the ‘IP Next Generation’ study. The staggeringly large numbers of connected devices we see today were certainly within the range predicted by that exercise. Doubtless, these device numbers will continue to grow. We continue to increase silicon chip production volumes and at the same time, we continue to refine the production process. But, at that time, we also predicted that the only way we could make the Internet work across such a massive pool of connected devices was to deploy a new IP protocol with a massively larger address space. From that reasoning, IPv6 was designed, as this world of abundant silicon processors was the issue that IPv6 was primarily intended to solve. The copious volumes of address space were designed to allow us to uniquely assign a public IPv6 address to every such device, no matter how small, or in whatever volume they might be deployed.
However, while the Internet has grown at such amazing speed, the deployment of IPv6 continues at a more measured pace. There is still no evidence of any common sense of urgency about the deployment of this protocol, and still, there is no common agreement that the continued reliance on IPv4 is failing us. Much of the reason for this apparent contradiction between the designed population of the IPv4 Internet and the actual device count, which is many times larger, is that the Internet rapidly changed from a peer-to-peer architecture to a client/server paradigm.
Clients can initiate network transactions with servers but cannot initiate transactions with other clients. Network Address Translators (NATs) are a natural fit for this client/server model, where pools of clients share a smaller pool of public addresses, and only require the use of an address while they have an active session with a remote server. NATs are the reason why over 30B connected devices can be squeezed into 3B advertised IPv4 addresses. Applications that cannot work behind NATs are no longer useful in the context of the public Internet and are no longer used as a result.
However, the pressures of this inexorable growth in the number of deployed devices in the Internet means that even NATs cannot absorb these growth pressures forever. NATs can extend the effective addressable space by up to 32 ‘extra’ bits using mapping of the source and destination port fields of the TCP and UDP headers, and they enable the time-based sharing of public addresses. Both of these measures are effective in stretching the IPv4 address space to encompass a larger client device pool, but they do not transform the address space into an infinitely elastic resource.
The inevitable outcome of this process is that we may see the fragmenting of the IPv4 Internet into several disconnected parts, probably based on the service ‘cones’ of the various points of presence of the content distribution servers, so that the entire concept of a globally unique and coherent address pool layered over a single coherent packet transmission realm will be foregone. Alternatively, we may see these growth pressures motivate the further deployment of IPv6, and the emergence of IPv6-only elements of the Internet as the network itself tries to maintain a cohesive and connected whole. Commercial pressures are pulling the network in both directions, so it’s entirely unclear what path the Internet will follow in the coming years, but my (admittedly cynical and perhaps overly jaded) personal opinion lies in the future of a highly fragmented network.
Can address allocation data help us to shed some light on what is happening in the larger Internet? Let’s look at what happened in 2024.
IPv4 in 2024
It appears that the process of exhausting the remaining pools of unallocated IPv4 addresses is proving to be as protracted as the process of the transition to IPv6. However, by the end of 2021, the end of the old registry allocation model had effectively occurred with the depletion of the residual pools of unallocated addresses in each of the Regional Internet Registries (RIRs).
It is difficult to talk about ‘allocations’ in today’s Internet. There is still a set of transactions where addresses are drawn from the residual pools of RIR-managed available address space and allocated or assigned to network operators, but at the same time, there is also a set of transactions where addresses are traded between networks in what is essentially a sale. These address transfers necessarily entail a change of registration details, so the registry records the outcome of a transfer, or sale, in a manner that is similar to an allocation or assignment.
If we want to look at the larger picture of the amount of IPv4 address space that is used or usable by Internet network operators, then perhaps the best metric to use is the total span of allocated and assigned addresses, and the consequent indication of annual change in the change in this total address span from year to year.
What is the difference between ‘allocated’ and ‘assigned’?
When a network operator or sub-registry has received an allocation, it can further delegate that IP address space to its customers along with using it for its own internal infrastructure. When a network operator has received an assignment, this can only be used for its own internal infrastructure.
I personally find the distinction between these two terms somewhat of a distracting artifice these days, so from here on I’ll use the term ‘allocation’ to describe both allocations and assignments, without further distinction.
For the first time in the IPv4 Internet, the total IPv4 allocated address pool contracted by 400,000 addresses in 2023, with 3.685B allocated addresses at the end of the year. This represented a contraction of 0.01% for the total allocated IPv4 public address pool, a contraction that was countered by a comparable rise in the span of allocated addresses through 2024 (Table 1).
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| Address span (billions) | 3.227 | 3.395 | 3.483 | 3.537 | 3.593 | 3.624 | 3.643 | 3.657 | 3.657 | 3.682 | 3.684 | 3.685 | 3.687 | 3.686 | 3.687 |
| Annual change (millions) | 241.7 | 168.0 | 88.4 | 53.9 | 55.9 | 30.6 | 19.4 | 13.2 | 0.6 | 24.9 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 1.6 | -0.4 | 1.2 |
| Relative growth | 8.1% | 5.2% | 2.6% | 1.5% | 1.6% | 0.85% | 0.53% | 0.36% | 0.02% | 0.68% | 0.06% | 0.03% | 0.04% | 0.01% | 0.03% |
Table 1 — IPv4 allocated addresses by year.
Have we exhausted all the available sources of further IPv4 addresses? The address management model is that unallocated addresses are held in a single pool by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), and blocks of addresses are passed to RIRs who then allocate them to various end entities, either for their own use or for further allocation. But, IANA exhausted the last of its available address pools some years ago, and these days it holds just 3 /24 address prefixes, and has done so for the past 12 years. Because the option of dividing this tiny address pool into five equal chunks of 153.6 individual addresses is not viable, then these addresses are likely to sit in the IANA Recovered Address registry for some time.
That is until one or more of the RIRs returns more prefixes recovered from the old ‘legacy’ allocated addresses to IANA, who would then be able to divide the pool equally and distribute them to each of the five RIRs. This is unlikely to occur.
Some addresses have been marked by IANA as reserved. This includes blocks of addresses reserved for Multicast use. At the top end of the IPv4 address space registry, there is a set of addresses that are marked as reserved for Future Use. This is a relatively large pool of 268,435,456 addresses (the old former ‘Class E’ space) and if ever there was a ‘future’ for IPv4 then it has well and truly come and gone. But exactly how to unlock this space and return it to the general use pool is a problem that so far has not found a generally workable solution, although efforts to do so have surfaced in the community from time to time.
The topic of releasing the Class E space for use in the public Internet as a globally routable unicast address space has been raised from time to time over the past 15 years or so. Some Internet drafts were published for the IETF’s consideration that either directly proposed releasing this space for use, or outlined the impediments in various host and router implementations that were observed to exist in 2008 when these drafts were being developed.
The proposals lapsed, probably due to the larger consideration at the time that the available time and resources to work on these issues were limited and the result of effort spent in ‘conditioning’ this IPv4 space for general use was only going to obtain a very small extension in the anticipated date of depletion of the remaining IPv4 address pools, while the same amount of effort spent on working on advancing IPv6 deployment was assumed to have a far larger beneficial outcome.
From time to time this topic reappears on various mailing lists and blogs (see this example), but the debates tend to circle around this same set of topics one more time, and then lapse.
As IANA is no longer a source of addresses, then we need to look at the RIR practices to see the life cycle of addresses from the registry’s perspective. When IP address space is returned to the RIR or reclaimed by the RIR according to the RIR’s policies it is normally placed in a RIR-reserved pool for some time and marked as reserved by the RIR. Marking returned or recovered addresses as reserved for some time allows various address prefix reputation and related services, including routing records, and time to record the cessation of the previous state of the address prefix, before any subsequent allocation. Following this quarantine period, this reserved space is released for reuse.
The record of annual year-on-year change in allocated addresses per RIR over the same thirteen-year period is shown in Table 2. There are some years when the per-RIR pool of allocated addresses shrunk in size. This is typically the result of address movement between RIRs, either due to administrative changes in some cases or address transfers between RIRs in others.
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| APNIC | 119.5 | 101.0 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 4.6 | 7.4 | 6.7 | 3.2 | 0.4 | 10.5 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 0.8 | -1.1 | -0.8 |
| RIPE NCC | 52.3 | 40.5 | 37.8 | 1.0 | 33.8 | 4.7 | 4.1 | 3.7 | 0.3 | 12.0 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 4.7 | 6.2 | 5.0 |
| ARIN | 27.2 | 53.8 | 24.3 | 19.0 | -14.1 | 2.3 | -4.8 | -2.3 | -0.3 | -10.1 | -0.9 | -1.7 | -3.8 | -5.5 | -3.0 |
| LACNIC | 17.1 | 13.6 | 17.3 | 26.3 | 18.7 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 2.4 | 1.2 | -0.2 | -0.3 | -0.1 | 0.0 |
| AFRINIC | 8.8 | 9.4 | 8.5 | 6.3 | 12.8 | 15.0 | 11.9 | 7.1 | 0.2 | 10.1 | -0.2 | -0.9 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| TOTAL | 224.9 | 218.3 | 88.5 | 53.8 | 55.8 | 30.6 | 19.4 | 13.1 | 0.7 | 24.9 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 1.6 | -0.4 | 1.2 |
Table 2 — Annual change in IPv4 allocated addresses (millions), distribution by RIR.
Each of the RIRs is running through their final pools of IPv4 addresses. At the end of 2024, across the RIR system, there are 4.6M addresses in the available pool, held mainly in APNIC (3.6M) and AFRINIC (990K). Around 10.2M addresses are marked as Reserved, with 4.6M held by ARIN and 4.4M addresses held by AFRINIC. As seen in Table 3, there has been a reduction in the reserved pool for all RIRs, except AFRINIC, and the major reductions were seen in APNIC (1.7M) and ARIN (600K) in ARIN (98K).
| Available | Reserved | |||||
| RIR | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| APNIC | 2,503,424 | 2,469,120 | 3,647,488 | 1,514,752 | 2,202,624 | 416,256 |
| RIPE NCC | - | 1,024 | 256 | 737,496 | 708,872 | 677,160 |
| ARIN | 8,448 | 8,960 | 3,840 | 5,311,488 | 5,213,184 | 4,609,792 |
| LACNIC | 1,024 | 256 | 1,536 | 148,480 | 151,296 | 118,528 |
| AFRINIC | 1,403,136 | 1,201,664 | 990,976 | 4,104,960 | 4,186,112 | 4,443,648 |
| TOTAL | 3,916,032 | 3,681,024 | 4,644,096 | 11,817,176 | 12,462,088 | 10,265,384 |
Table 3 — IPv4 available and reserved pools, December 2024.
The RIR IPv4 address allocation volumes by year are shown in Figure 1, but it is challenging to understand precisely what is meant by an allocation across the entire RIR system as there are some subtle but important differences between RIRs, particularly as they relate to the handling of transfers of IPv4 addresses.
In the case of ARIN, a transfer between two ARIN-serviced entities is conceptually treated as two distinct transactions: A return of the addresses to the ARIN registry and a new allocation from ARIN. The date of the transfer is recorded as the new allocation date in the records published by the RIR. Other RIRs handle address transfers similarly to a change in the designated holder of already-allocated addresses. During the transfer process, the RIR’s records retain the original allocation date for the transferred addresses. When analysing individual transaction records from the published RIR data and grouping them by year, ARIN’s data reflects the volume of transferred addresses processed during that year. In contrast, data from other RIRs only includes the allocations made during that year.
To provide a view across the entire system it’s necessary to use an analysis approach that can compensate for these differences in the ways RIRs record address transactions. In this study, an allocation is defined here as a state transition in the registry records from reserved or available to an allocated state. This is intended to separate out the various actions associated with processing address transfers, which generally involve no visible state change, as the transferred address block remains allocated across the transfer, from allocations. This is how the data used to generate Figure 1 has been generated from the RIR published data, comparing the status of the address pools at the end of each year to that of the status at the start of the year. An allocation in that year is identified if the allocated address block was not registered as allocated at the start of the year.
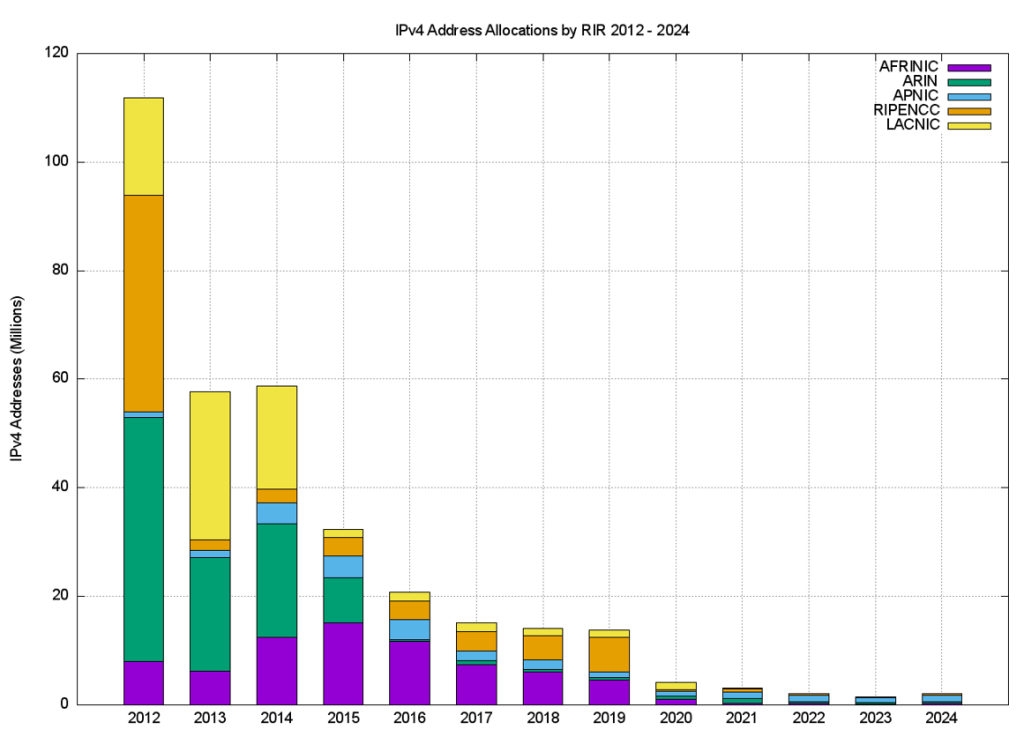
The number of RIR IPv4 allocations by year, generated using the same data analysis technique as Figure 1, is shown in Figure 2.
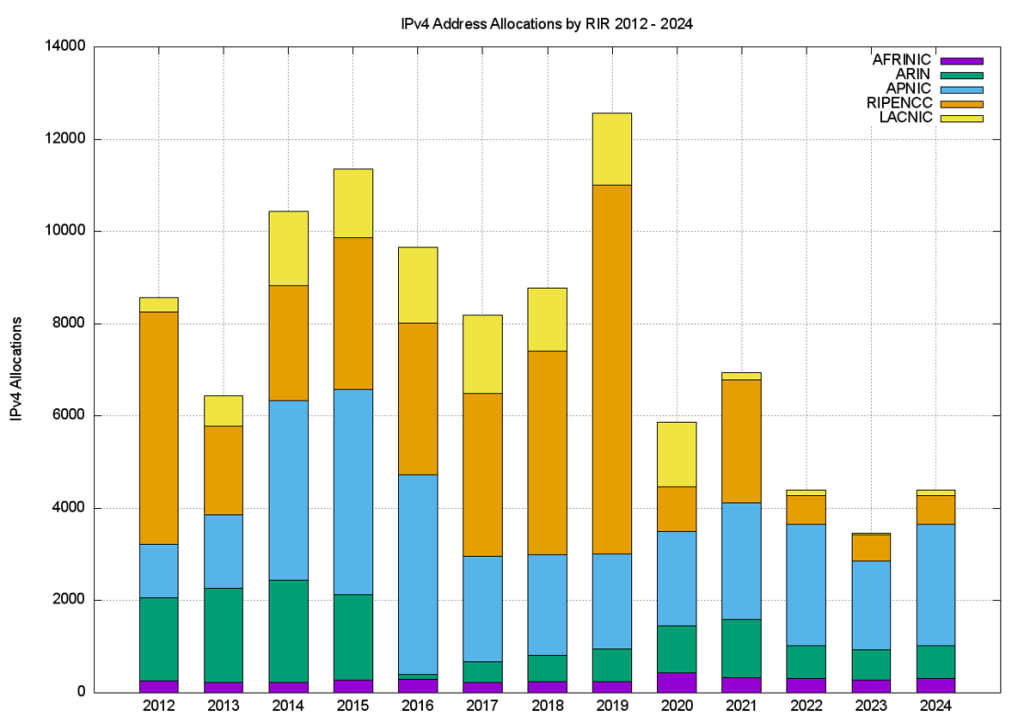
It is clear from these two figures that the average size of an IPv4 address allocation has shrunk considerably in recent years, corresponding to the various IPv4 address exhaustion policies in each of the RIRs.
IPv4 address transfers
In recent years, the RIRs have permitted the registration of IPv4 transfers between address holders, as a means of allowing secondary redistribution of addresses as an alternative to returning unused addresses to the registry. This has been in response to the issues raised by IPv4 address exhaustion, where the underlying motivation is to encourage the reuse of otherwise idle or inefficiently used address blocks through the incentives provided by a market for addresses and to ensure that such address movement is publicly recorded in the registry system.
The number of registered transfers in the past eleven years is shown in Table 4. This number of transfers includes both inter-RIR and intra-RIR transfers. It also includes both the merger and acquisition-based transfers and the other grounds for address transfers. Each transfer is treated as a single transaction, and in the case of inter-RIR transfers, this is accounted for in the receiving RIR’s totals.
| Recieving RIR | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| APNIC | 158 | 180 | 307 | 451 | 840 | 845 | 491 | 533 | 820 | 785 | 745 | 796 | 752 |
| RIPE NCC | 10 | 171 | 1,054 | 2,836 | 2,373 | 2,451 | 3,775 | 4,221 | 4,696 | 5,742 | 4,640 | 4,937 | 5,215 |
| ARIN | 3 | 22 | 26 | 26 | 68 | 94 | 150 | 141 | 97 | 185 | |||
| LACNIC | 2 | 3 | 9 | 17 | 20 | 17 | |||||||
| AFRINIC | 17 | 27 | 26 | 80 | 58 | 14 | 15 | ||||||
| Total | 168 | 351 | 1,361 | 3,290 | 3,235 | 3,322 | 4,311 | 4,849 | 5,639 | 6,766 | 5,601 | 5,864 | 6,184 |
Table 4 — IPv4 address transfer transactions per year.
The differences between RIRs reported numbers are interesting. The policies relating to address transfers do not appear to have been adopted to any significant extent by address holders in AFRINIC and LACNIC serviced regions, while uptake in the RIPE NCC service region appears to be very enthusiastic!
A slightly different view is that of the volume of addresses transferred per year (Table 5).
| Recieving RIR | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| APNIC | 1.6 | 2.3 | 4.1 | 6.6 | 8.2 | 4.9 | 10.0 | 4.3 | 16.6 | 6.5 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 2.5 |
| RIPE NCC | 0.1 | 2.0 | 9.6 | 11.6 | 9.2 | 24.6 | 19.5 | 26.9 | 18.2 | 16.2 | 36.9 | 20.8 | 23.0 |
| ARIN | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 3.1 | 1.6 | 4.5 | ||||
| LACNIC | 0.0 | ||||||||||||
| AFRINIC | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||||||
| Total | 1.7 | 4.3 | 13.7 | 18.2 | 17.6 | 29.7 | 29.7 | 31.9 | 36.2 | 26.4 | 44.3 | 25.3 | 30.2 |
Table 5 — Volume of transferred IPv4 addresses per year (Millions of addresses).
A plot of these numbers is shown in Figures 3 and 4.
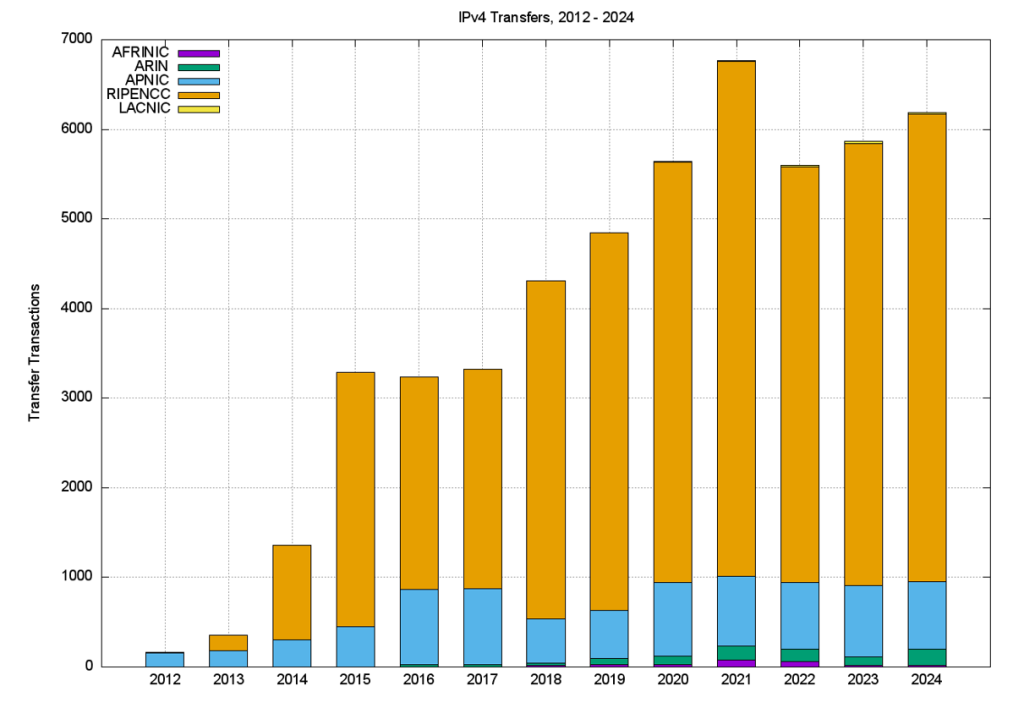
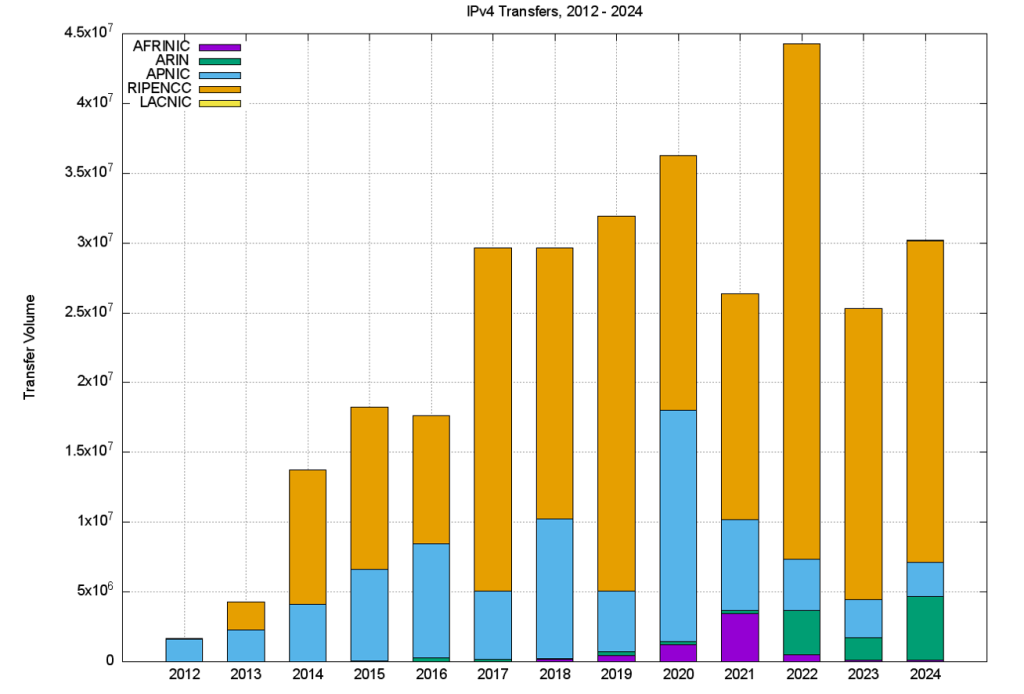
The volume of transferred addresses reached a peak in 2022 and declined in 2023. In the case of APNIC, the peak occurred in 2020, and the APNIC 2024 volume is comparable to the volume transferred in 2013. In the RIPE and ARIN regions, address transfers are still growing in total volume, while in APNIC the volume of IPv4 address transfers has largely waned.
The aggregate total of addresses that have been listed in these transfer logs since 2012 is 309M addresses, or the equivalent of 18.4 /8s, which is 8% of the total delegated IPv4 address space of 3.7B addresses. However, that figure is likely to be an overestimation, as several address blocks have been transferred multiple times over this period.
Are transfers performing unused address recovery?
This data raises some questions about the nature of transfers. The first question is whether address transfers have managed to be effective in dredging the pool of allocated but unadvertised public IPv4 addresses and recycling these addresses back into active use.
It was thought that by being able to monetize these addresses, holders of such addresses may have been motivated to convert their networks to use private addresses and resell their holding of public addresses. In other words, the opening of a market in addresses would provide an incentive for otherwise unproductive address assets to be placed on the market. Providers who had a need for addresses would compete with other providers who had a similar need in bidding to purchase these addresses. In conventional market theory, the most efficient user of addresses (here ‘most efficient’ is based on the ability to use addresses to generate the greatest revenue) would be able to set the market price. Otherwise, unused addresses would be put to productive use, and as long as demand outstrips supply the most efficient use of addresses is promoted by the actions of the market. In theory.
However, the practical experience with transfers is not so clear. The data relating to address recycling is inconclusive, in that between 2011 and late 2017 the pool of unadvertised addresses sat between 48 and 50 /8s. This pool of unadvertised addresses rose from the start of 2018 and by early 2020 there were just under 51 /8s that were unadvertised in the public Internet. This two-year period of increase in the unadvertised address pool appeared to be a period where IPv4 addresses were being hoarded, though such a conclusion from just this high-level aggregate date is highly speculative.
There was a substantial reduction in the size of this unadvertised address pool at the start of 2021. The major change in 2021 was the announcement in the Internet’s routing system of seven /8s from the address space originally allocated to the US Department of Defence in the early days of the then ARPANET. At the end of 2021, AS749 originated more IPv4 addresses than any other network, namely 211,581,184 addresses, or the equivalent of a /4.34 in prefix length notation, or 5% of the total IPv4 address pool. Across 2022 and 2023 the previous trend of an increasing pool of unadvertised addresses resumed. On 12 December 2024, a total of 81,224,704 addresses (the equivalent of 4.8 /8s) was advertised by Autonomous Systems (ASes) operated by Amazon, mainly AS16509, bringing the total pool of unadvertised addresses down to a level last observed in the year 2000.
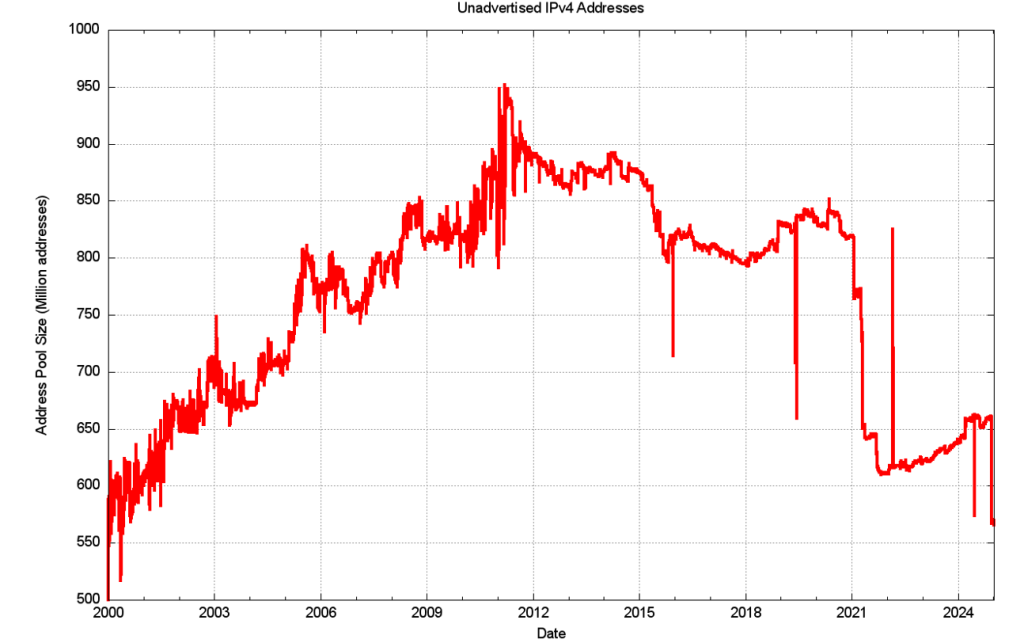
The larger picture of the three IPv4 address pool sizes, allocated, advertised, and unadvertised address pools since the start of 2000 is shown in Figure 6. The onset of more restrictive address policies coincides with the exhaustion of the central IANA unallocated address pool in early 2011, and the period since that date has seen the RIRs run down their address pools.
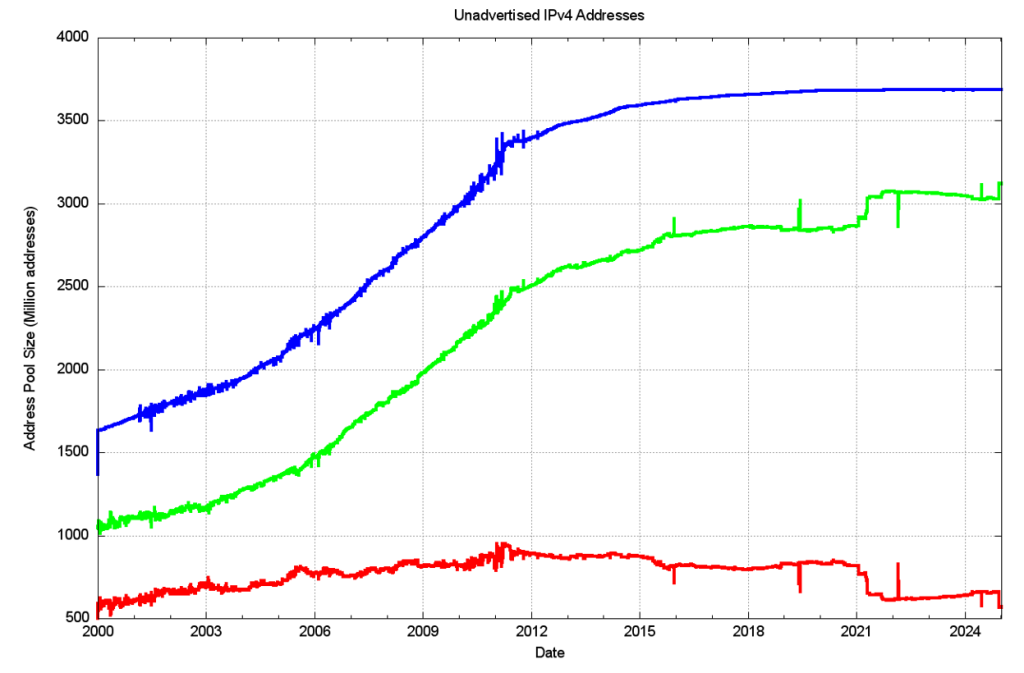
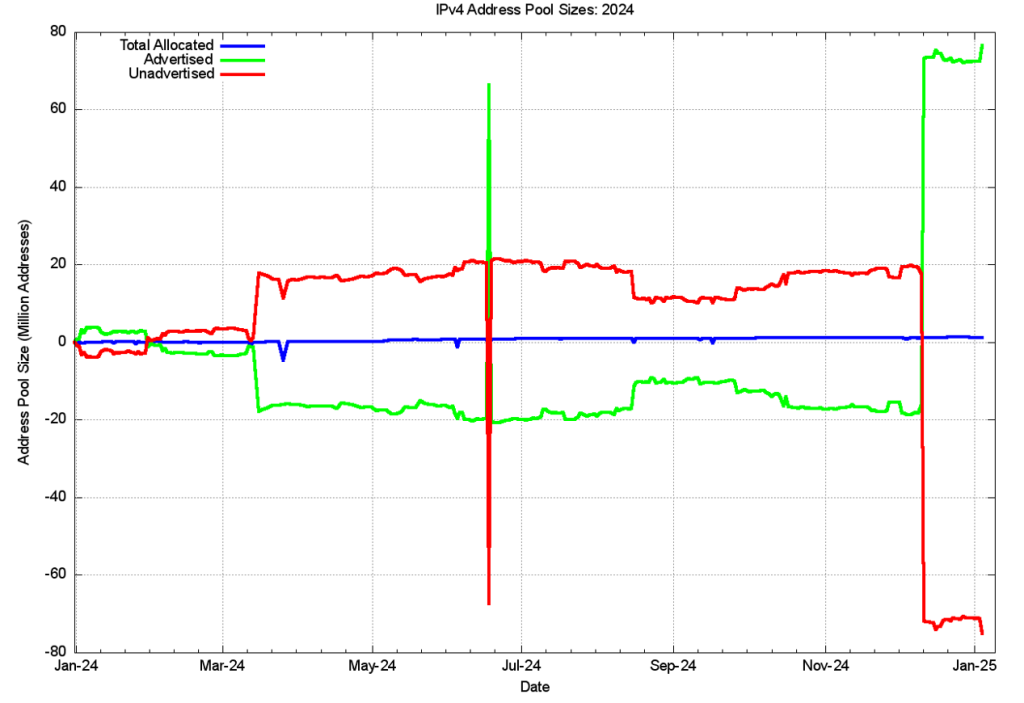
We can also look at 2024, looking at the changes in these address pools since the start of the year, as shown in Figure 7. The total span of advertised addresses was falling by 20M addresses through to 12 December, when the Amazon address range announcements changed the situation.
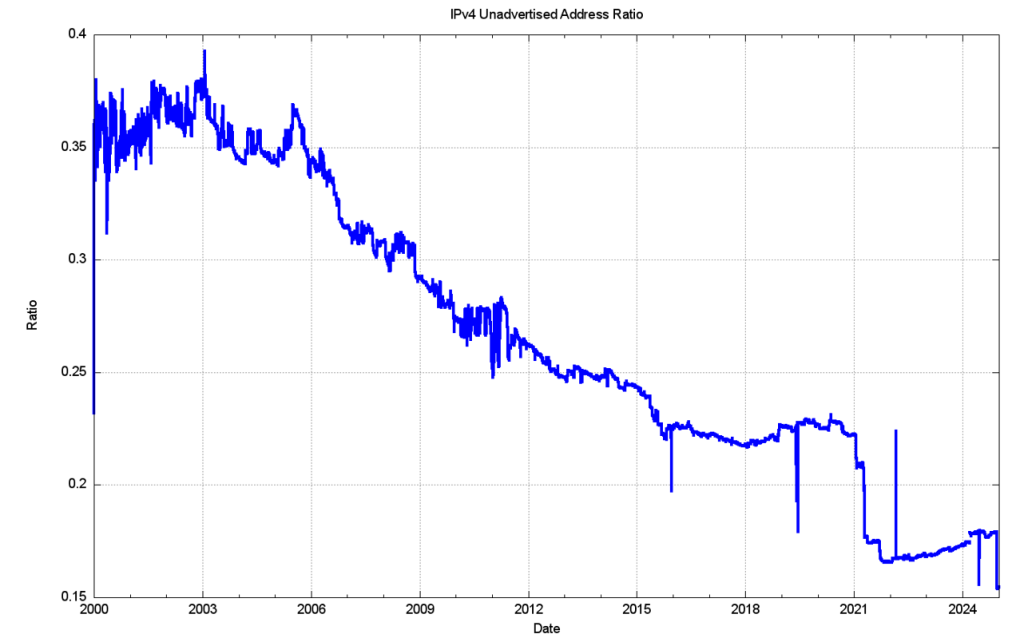
In relative terms, expressed as a proportion of the total pool of allocated IP addresses, the unadvertised address pool peaked at 38% of the total assigned address pool in early 2003 and then declined over the ensuing 15 years to a relatively low value of 22% at the start of 2018. The ratio has been steadily climbing since that date, with abrupt falls due to the advertisement of the legacy US Department of Defence address space in 2021, and the Amazon address announcements in December 2024 (Figure 8).
This data also shows a somewhat sluggish transfer market. The number of transfer transactions is rising, but the total volume of transferred addresses is falling for most RIRs, with the exception of the RIPE NCC (Tables 4 and 5). The address market does not appear to have been all that effective in flushing out otherwise idle addresses and redeploying them into the routed network.
However, as with all other commodity markets, the market price of the commodity reflects the balancing of supply and demand and the future expectations of supply and demand. What can be seen in the price of traded IPv4 addresses over the past eight years?
One of the address brokers, Hilco Streambank, publishes the historical price information of transactions (if only all the address brokers did the same, as a market with open price information for transactions can operate more efficiently and fairly than markets where price information is occluded). Figure 9 uses the Hilco Streambank transaction data to produce a time series of address prices.
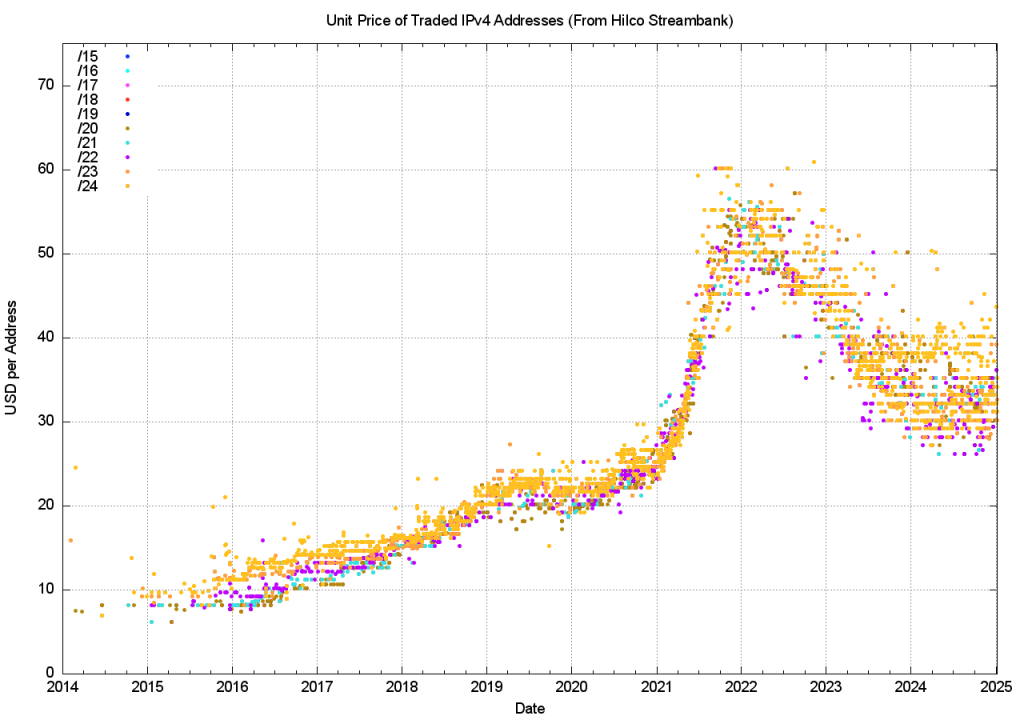
There are several distinct behaviour modes in this time series data. The initial data prior to 2016 reflected a relatively low volume of transactions with stable pricing of just below USD 10 per address. Over the ensuing four years, up to the start of 2019, the unit price doubled, with small blocks (/24s and /23s) attracting a price premium. The price stabilized for the next 18 months at between USD 20 to USD 25 per address, with large and small blocks trading at a similar unit price. The 18 months from mid-2020 up to the start of 2022 saw a new dynamic that was reflective of an exponential rise in prices, and the unit price lifted to between USD 45 and USD 60 per address by the end of 2021. The year 2022 saw the average market price drop across the year, but the variance in prices increased and trades at the end of the year were recorded at prices of between USD 40 to USD 60 per address.
This price decline continued across 2023, and by the end of 2023, IPv4 addresses were traded at unit prices of between USD 26 to USD 40. The prices of addresses across 2024 were relatively stable, and this is shown in a view of the average unit price of addresses per month for each prefix size over 2023 and 2024 (Figure 10).
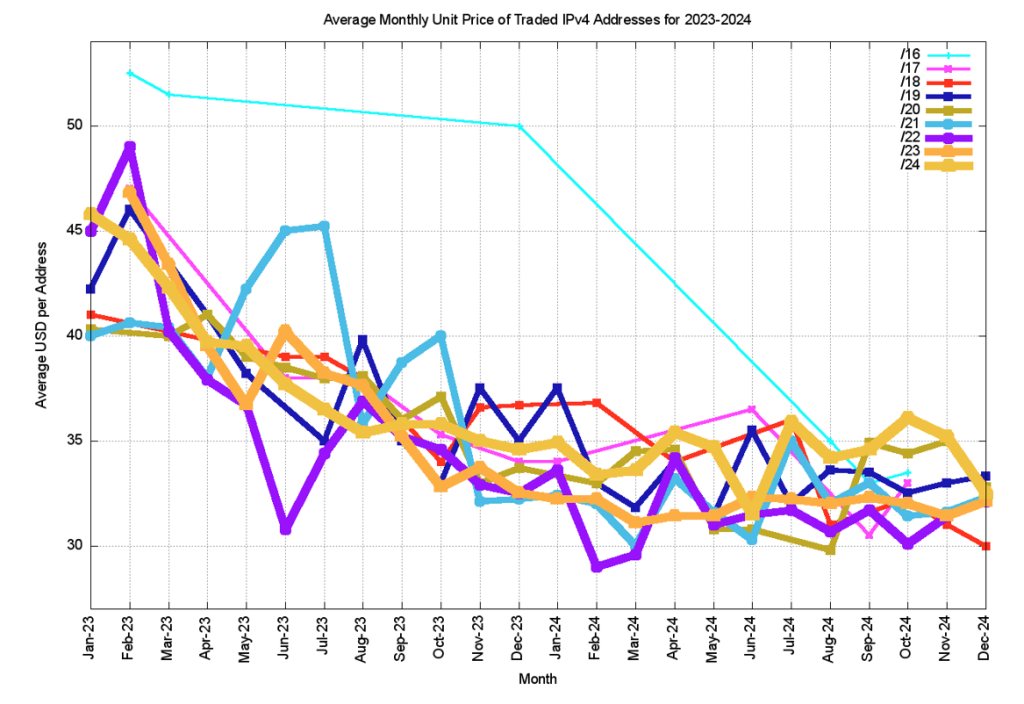
If prices are reflective of supply and demand it appears that demand has increased at a far greater level than supply, and the price escalation across 2021 reflects some form of perceived scarcity premium being applied to addresses in recent times. However, the subsequent price slump shows that this perception was short-lived, and the average unit price movement of USD 2.50 per year appears to have been resumed in 2024.
Is the supply of tradable IPv4 addresses declining? One way to provide some insight into answering this question is to look at the registration age of transferred addresses. Are such addresses predominately recently allocated addresses, or are they longer-held address addresses where the holder is wanting to realize the inherent value in otherwise unused assets? The basic question concerns the age distribution of transferred addresses where the age of an address reflects the period since it was first allocated or assigned by the RIR system.
The cumulative age distribution of transferred addresses by transaction is shown on a year-by-year basis in Figures 11 and 12.
In the period 2019 to 2021, a visible subset of address holders appeared to hold recently allocated addresses for the policy-mandated minimum holding period of two years, and then transfer these addresses on the market. In previous years 8% of addresses that were transferred were originally allocated up to five years prior to the transfer. In 2022 this number has fallen to 4%, which is presumably related to the smaller volumes of address allocations in 2022 rather than any change in behaviours of address holders, and in 2023 and 2024 this behaviour has all but disappeared, due to the very small volume of address allocations by the RIRs rather than any change in the behaviour of address holders.
The bulk of transferred addresses in 2024 (more than 50% of the total volume) were originally allocated between 15 and 22 years ago or between 2003 and 2010.
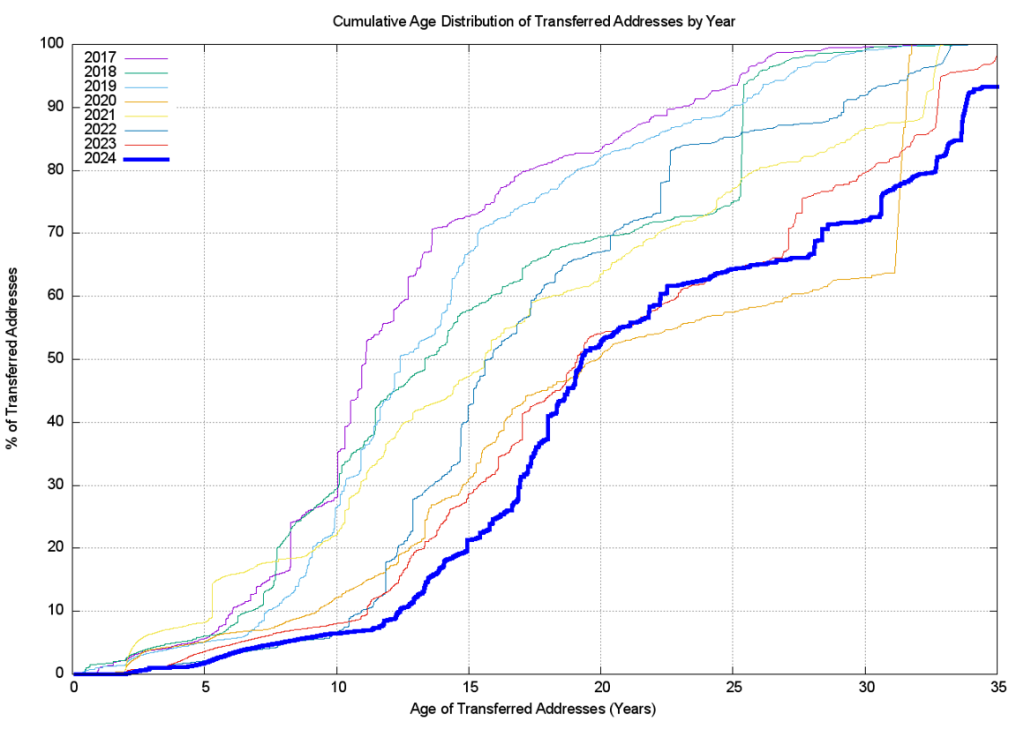
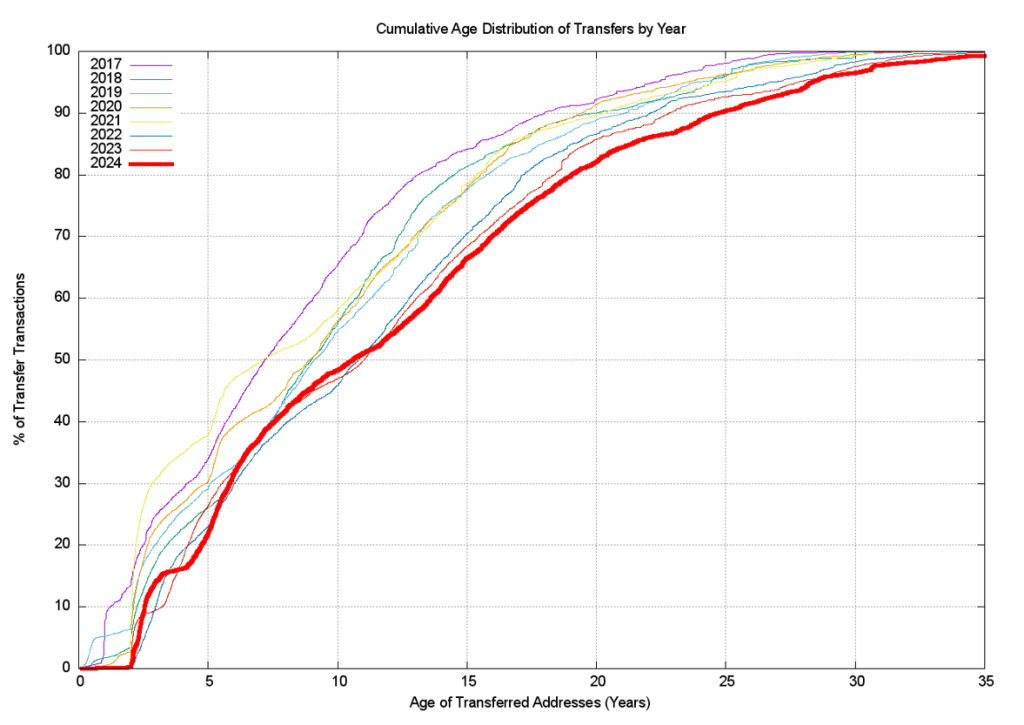
Figure 12 shows the cumulative age distribution of transfer transactions, and the disparity between the two distributions for 2024 shows that recent individual allocations have been far smaller in size but are still being traded. 20% of the recorded transfer transactions in 2024 refer to an address prefix that was allocated within the past five years, yet these transactions encompass less than 2% of the inventory of transferred addresses in 2024. 48% of the volume of transferred addresses were originally allocated 20 or more years ago, while these transactions are recorded in just 17% of the transfers recorded in 2024.
There appear to be several motivations driving the transfer process.
One is when demand outstrips supply and price escalation is an inevitable consequence. This may motivate some network operators to purchase addresses early, in the expectation that further delay will encounter higher prices. This factor also may motivate some address holders to defer the decision to sell their addresses, in that delay will improve the price. Taken together, these motivations can impair market liquidity and create a feedback loop that causes price escalation. This appears to have been the case in 2021.
The second factor is IPv6 deployment. Many applications prefer to use IPv6 over IPv4 if they can (the so-called ‘Happy Eyeballs’ protocol for protocol selection). For a dual-stack access network, this means that the more the services that they use are provisioned with dual-stack, then the lower the traffic volume that uses IPv4, and the lower the consumption pressure on their IPv4 CG-NAT address pools, which reduces their ongoing demand for IPv4 address space. This reduced demand for additional IPv4 addresses has an impact on the market price. A falling market price acts as a motivation for sellers to bring their unused address inventory to market sooner, as further delay will only result in a lower price.
The overriding feature of this address market is the level of uncertainty within the market over the state of the IPv6 transition, coupled with the uncertainty over the further growth of the network. This high degree of uncertainty may lie behind the very high variance of individual transfer transaction prices, as shown in Figure 9. However, this uncertainty was resolved to some extent across 2023, and levels of demand appear to have dissipated in the past 12 months through 2024. Have we finally managed to deploy enough network infrastructure in both IPv4 and IPv6 to get ahead of the demand pressures? Are we, perhaps for the first time, looking at a market that is currently saturated with sufficient addresses and associated service platform infrastructure.
Do transfers fragment the address space?
The next question is whether the transfer process is further fragmenting the address space by splitting up larger address blocks into successively smaller address blocks. There are 50,942 transactions described in RIR transfer registries from the start of 2012 until the start of 2025, and of these 12,559 entries list transferred address blocks that are smaller than the original allocated block. In other words, 25% of transfers implicitly perform fragmentation of the original allocation.
These 12,559 transfer entries that have fragmented the original allocation are drawn from 6,578 original allocations. On average the original allocation is split into two smaller address blocks. This data implies that the answer to this question is that address blocks are being fragmented as a result of address transfers, but in absolute terms, this is not a major issue. There are 246,218 distinct IPv4 address allocation records in RIR registries as of the end of 2024, and the fragmentation reflected in 12,559 more specific entries of original allocation address blocks represents around 5.1% of the total pool of allocated address prefixes.
Imports and exports of addresses
The next question concerns the international flow of transferred addresses. Let’s look at the ten economies that sourced the greatest volume of transferred addresses, irrespective of their destination (including ‘domestic’ transfers within the same economy) (Table 6), and the ten largest recipients of transfers (Table 7), and the ten largest international address transfers (Table 8). We will use the RIR-published transfer data for the year 2024 as the basis for these tables.
| Rank | CC | Addresses | Source economy |
| 1 | US | 8,136,704 | USA |
| 2 | GB | 3,013,120 | UK |
| 3 | PL | 2,682,880 | Poland |
| 4 | RO | 1,783,296 | Romania |
| 5 | JP | 1,739,264 | Japan |
| 6 | DE | 1,509,120 | Germany |
| 7 | NL | 1,117,184 | Netherlands |
| 8 | AU | 1,069,824 | Australia |
| 9 | IR | 975,616 | Iran |
| 10 | CH | 905,728 | Switzerland |
Table 6 — Top 10 economies sourcing transferred IPv4 addresses in 2024.
| Rank | CC | Addresses | Destination economy |
| 1 | GB | 7,526,912 | UK |
| 2 | US | 5,853,440 | USA |
| 3 | PL | 2,017,536 | Poland |
| 4 | DE | 1,620,992 | Germany |
| 5 | RO | 1,510,656 | Romania |
| 6 | NL | 962,816 | Netherlands |
| 7 | JP | 817,408 | Japan |
| 8 | IR | 800,768 | Iran |
| 9 | AU | 702,720 | Australia |
| 10 | NO | 670,464 | Norway |
Table 7 — Top 10 economies receiving transferred IPv4 addresses in 2024.
There are many caveats about this data collection, particularly relating to the precise meaning of this economy-based geolocation. Even if we use only the CC entry in RIR registry records, then we get a variety of meanings. Some RIRs use the principle that the recorded CC entry corresponds to the physical location of the headquarters of the nominated entity that is the holder of the addresses, irrespective of the locale where the addresses are used on the Internet. Other RIRs allow the holder to update this geolocation entry to match the holder’s intended locale where the addresses will be used. It is generally not possible to confirm the holder’s assertion of location, so whether these self-managed records reflect the actual location of the addresses or reflect a location of convenience is not always possible to determine.
When we look at the various geolocation services, of which Maxmind is a commonly used service, there are similar challenges in providing a geographic location service. At times this is not easy to establish, such as with tunnels used in VPNs. Is the ‘correct’ location the location of the tunnel ingress or tunnel egress? Many of the fine-grained differences in geolocation services reflect the challenges in dealing with VPNs and the various ways these location services have responded. There is also the issue of cloud-based services. Where the cloud service uses anycast, then the address is in many locations at once. In the case where the cloud uses conventional unicast, the addresses use may be fluid across the cloud service’s points of presence based on distributing addresses to meet the demands for the service. The bottom line is that these location listings are a ‘fuzzy’ approximation rather than a precise indication of location.
With that in mind let’s now look at imports and exports of addresses of 2024 transfers where the source and destination of the transfers are in different economies. 1,928 transfers appear to result in a movement of addresses between economies, involving a total of 11,467,008 addresses, as shown in Table 8.
| Rank | From | To | Addresses (M) | Source | Destination |
| 1 | US | GB | 4,845,568 | USA | UK |
| 2 | PL | US | 656,640 | Poland | USA |
| 3 | JP | US | 646,144 | Japan | USA |
| 4 | GB | SE | 533,248 | UK | Sweden |
| 5 | CH | US | 459,008 | Switzerland | USA |
| 6 | UA | US | 448,000 | Ukraine | USA |
| 7 | NL | GB | 264,704 | Netherlands | UK |
| 8 | RO | ES | 262,656 | Romania | Spain |
| 9 | AU | DE | 262,144 | Australia | Germany |
| 10 | GB | US | 254,208 | UK | USA |
| 11 | US | SG | 144,640 | USA | Singapore |
| 12 | JP | GB | 131,072 | Japan | UK |
| 13 | DE | US | 125,440 | Germany | USA |
| 14 | IR | AE | 98,304 | Iran | UAE |
| 15 | DE | SE | 68,608 | Germany | Sweden |
| 16 | AU | GB | 67,840 | Australia | UK |
| 17 | US | RU | 67,328 | USA | Russian Federation |
| 18 | NZ | US | 65,792 | New Zealand | USA |
| 19 | CA | DE | 65,536 | Canada | Germany |
| 20 | CH | IE | 65,536 | Switzerland | Ireland |
Table 8 — Top 20 economy-to-economy IPv4 address transfers in 2024.
The 2024 transfer logs also contain 4,257 domestic address transfers, with a total of 18,719,040 addresses, with the largest activity by address volume in domestic transfers in the USA (29M), UK (20M), Poland (2M), Romania (1.5M) and Germany (1.2M).
An outstanding question about this transfer data is whether all address transfers that have occurred have been duly recorded in the registry system. This question is raised because registered transfers require conformance to various registry policies, and it may be the case that only a subset of transfers are being recorded in the registry as a result. This can be somewhat challenging to detect, particularly if such a transfer is expressed as a lease or other form of temporary arrangement, and if the parties agree to keep the details of the transfer confidential.
It might be possible to place an upper bound on the volume of address movements that have occurred in any period by looking at the Internet’s routing system. One way to shed some further light on what this upper bound on transfers might be is through a simple examination of the routing system, looking at addresses that were announced in 2024 by comparing the routing table state at the start of the year with the end of the year (Table 9).
| Jan-24 | Jan-25 | Delta | Unchanged | Rehome | Removed | Added | |
| Announcements | 944,174 | 995,963 | 51,789 | 838,184 | 24,561 | 81,879 | 133,128 |
| Address span (/8s) | 4,142.89 | 4,269.81 | 126.91 | 3,880.42 | 37.93 | 105.46 | 225.25 |
| Root prefixes | 456,547 | 469,272 | 12,725 | 403,293 | 17,694 | 29,275 | 48,015 |
| More specifics | 487,627 | 526,691 | 39,064 | 434,891 | 6,687 | 52,604 | 85,113 |
| Address span (/8s) | 846.95 | 899.75 | 52.80 | 728.76 | 9.56 | 86.79 | 116.65 |
Table 9 — IPv4 BGP changes over 2024.
While the routing table grew by 51,789 entries over the year, the nature of the change is slightly more involved. 81,879 prefixes that were announced at the start of the year were removed from the routing system at some time throughout the year, and 133,128 prefixes were announced by the end of the year that were not announced at the start of the year. More transient prefixes may have appeared and been withdrawn throughout the year of course, but here we are comparing two snapshots rather than looking at every update message. A further 24,561 prefixes had changed their originating ASN, indicating some form of change in the prefix’s network location in some manner.
If we look at the complete collection of BGP updates seen from an individual BGP vantage point (AS131072) across all of 2024 we see a larger collection of transient address prefixes. A total of 1,830,657 distinct prefixes were observed through 2024. That implies that 886,483 additional prefixes were seen at some point through the year, from the initial set at the start of the year.
We can compare these prefixes that changed in 2024 against the transfer logs for the two-year period 2023 and 2024. Table 10 shows the comparison of these routing numbers against the set of transfers that were logged in these two years.
| Type | Listed | Unlisted | Ratio |
| Rehomed | |||
| All | 955 | 23,011 | 4.0% |
| Root prefixes | 459 | 11,172 | 3.9% |
| Removed | |||
| All | 971 | 80,908 | 1.2% |
| Root prefixes | 464 | 28,811 | 1.6% |
| Added | |||
| All | 2,539 | 130,589 | 1.9% |
| Root prefixes | 1,872 | 46,143 | 3.9% |
Table 10 — Routing changes across 2024 compared to the transfer log entries for 2023 – 2024.
These figures show that 1% to 4% of changes in advertised addresses from the beginning to the end of the year are reflected as changes as recorded in RIR transfer logs. This shouldn’t imply that the remaining changes in advertised prefixes reflect unrecorded address transfers. There are many reasons for changes in the advertisement of an address prefix and a change in the administrative controller of the address is only one potential cause. However, it does establish some notional upper ceiling on the number of movements of addresses in 2024, some of which relate to the transfer of operational control of an address block, that has not been captured in the transfer logs.
Finally, we can perform an age profile of the addresses that were added, removed and re-homed during 2024 and compare it to the overall age profile of IPv4 addresses in the routing table. This is shown in Figure 13. This figure shows that address prefixes added to the routing table tend to be ‘younger’ than average. One-half of all added address prefixes are 12-years-old, while for all advertised address prefixes 50% of such prefixes are 17-years-old or younger. Prefixes that are changing their originating network (‘re-Homing’) tend to be older than average, and 50% of all re-homed prefixes are 22 years old or older.
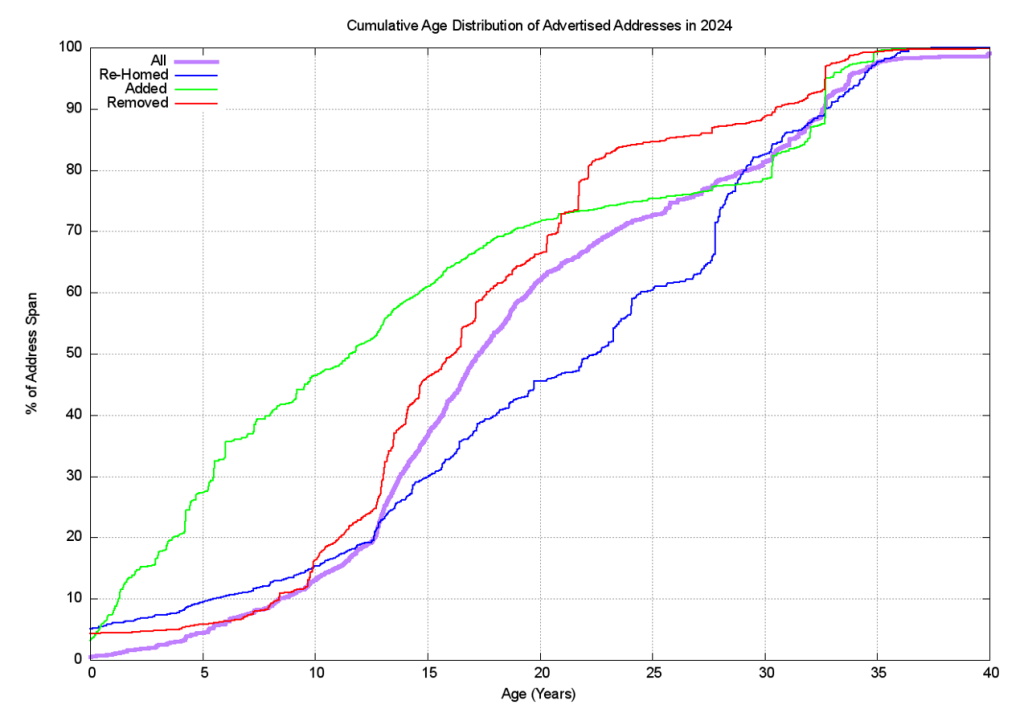
As IPv4 moves into its final stages we are perhaps now able to take stock of the overall distribution of IPv4 addresses and look at where the addresses landed up. Table 11 shows the ten economies that have the largest pools of allocated IPv4 addresses. However, I have to note that the assignation of a CC in an address registration reflects the economy where the address holder is located (the corporate location), and not necessarily the economy where the addresses will be deployed.
| Rank | CC | IPv4 pool | % Total | Per capita | Economy |
| 1 | US | 1,611,699,808 | 43.7% | 4.70 | USA |
| 2 | CN | 343,161,088 | 9.3% | 0.24 | China |
| 3 | JP | 189,000,960 | 5.1% | 1.55 | Japan |
| 4 | GB | 134,198,664 | 3.6% | 1.97 | UK |
| 5 | DE | 124,111,552 | 3.4% | 1.49 | Germany |
| 6 | KR | 112,504,320 | 3.1% | 2.18 | Republic of Korea |
| 7 | BR | 87,145,472 | 2.4% | 0.40 | Brazil |
| 8 | FR | 82,068,336 | 2.2% | 1.26 | France |
| 9 | CA | 67,990,016 | 1.8% | 1.73 | Canada |
| 10 | IT | 54,034,240 | 1.5% | 0.92 | Italy |
Table 11 — IPv4 allocated address pools per national economy as of January 2025.
If we divide this address pool by the current population of each national entity, then we can derive an address per capita index. The global total of 3.69B allocated addresses with an estimated global population of 8B people gives an overall value of 0.46 IPv4 addresses per capita.
| Rank | CC | IPv4 pool | % Total | Per capita | Economy |
| 1 | SC | 7,475,456 | 0.2% | 68.86 | Seychelles |
| 2 | VA | 10,752 | 0.0% | 20.33 | Holy See |
| 3 | GI | 235,264 | 0.0% | 7.19 | Gibraltar |
| 4 | VG | 166,144 | 0.0% | 5.21 | British Virgin Islands |
| 5 | US | 1,611,699,808 | 43.7% | 4.70 | USA |
| 6 | SG | 26,597,376 | 0.7% | 4.38 | Singapore |
| 7 | MU | 4,780,032 | 0.1% | 3.67 | Mauritius |
| 8 | SE | 31,078,888 | 0.8% | 2.90 | Sweden |
| 9 | CH | 25,444,472 | 0.7% | 2.87 | Switzerland |
| 10 | NO | 15,542,032 | 0.4% | 2.81 | Norway |
| Total | XA | 3,687,386,072 | 100.0% | 0.45 | World |
Table 12 — IPv4 allocated address pools ranked by per-capita holdings.
IPv4 address leasing
It is worth noting that the address market includes leasing as well as sales. Should an entity that requires IPv4 addresses enter the market and perform an outright purchase of the addresses from an existing address holder, or should they execute a timed lease to have the use of these addresses for a specified period and presumably return these addresses at the end of the lease? This lease versus buy question is a very conventional question in market economics and there are various well-rehearsed answers to the question. They tend to relate to the factoring of market information and scenario planning.
If a buyer believes that the situation that led to the formation of a market will endure for a long time, and the goods being traded on the market are in finite supply while the level of demand for these goods is increasing, then the market will add an escalating scarcity premium to the price goods being traded. The balancing of demand and supply becomes a function of this scarcity premium imposed on the goods being traded. Goods in short supply tend to become more expensive to buy over time. A holder of these goods will see an increase in the value of the goods that they hold. A lessee will not.
If a buyer believes that the market only has a short lifespan, and that demand for the good will rapidly dissipate at the end of this lifespan, then leasing the good makes sense, in so far as the lessee is not left with a valueless asset when the market collapses.
Scarcity also has several additional consequences, one of which is the pricing of substitute goods. At some point, the price of the original good rises to the point that substitution looks economically attractive, even if the substitute good has a higher cost of production or use. In fact, this substitution price effectively sets a price ceiling for the original scarce good.
Some commentators have advanced the view that an escalating price for IPv4 increases the economic incentive for IPv6 adoption, and this may indeed be the case. However, there are other potential substitutes that have been used, most notably NATs. While NATs do not eliminate the demand pressure for IPv4, they can go a long way to increase the address use efficiency of IPv4 addresses. NATs allow the same address to be used by multiple customers at different times. The larger the pool of customers that share a common pool of NAT addresses the greater the achievable multiplexing capability.
Estimating how long the IPv4 address market will persist essentially depends on two factors — how long IPv4 and NATs remain viable, and how quickly IPv6 is deployed widely enough to support IPv6-only services. There is likely to be a tipping point where the pressure for all hosts and networks to support access to services over IPv4 collapses. At that point, the early IPv6-only adopters can dump all their remaining IPv4 resources onto the market as they have no further need for them, which would presumably trigger a level of market panic to emerge as existing holders are faced with the prospect of holding a worthless asset and are therefore under pressure to sell off their IPv4 assets while there are still buyers in the market.
While a significant population of IPv4-only hosts and networks can stall this transition and increase scarcity pressure, if the scarcity pressure becomes too great the impetus of IPv6-only adoption increases to the level that the IPv6-connected base achieves market dominance. When this condition is achieved the IPv4 address market will quickly collapse.
IPv6 in 2024
Obviously, the story of IPv4 address allocations is only half of the story, and to complete the picture it’s necessary to look at how IPv6 has fared over 2024.
IPv6 uses a somewhat different address allocation methodology than IPv4, and it is a matter of choice for a service provider as to how large an IPv6 address prefix is assigned to each customer. The original recommendations published by the IAB and IESG in 2001, documented in RFC 3177, envisaged the general use of a /48 prefix as a generally suitable end-site prefix. Subsequent consideration of long-term address conservation saw a more flexible approach being taken with the choice of the end site prefix size being left to the service provider. Today’s IPv6 environment has some providers using a /60 end site allocation unit, many using a /56, and many other providers using a /48. This variation makes a comparison of the count of allocated IPv6 addresses somewhat misleading, as an ISP using /48s for end sites will require 256 times more address space to accommodate a similarly sized customer base as a provider who uses a /56 end site prefix, and 4,096 times more address space than an ISP using a /60 end site allocation!
For IPv6 let’s use both the number of discrete IPv6 allocations and the total amount of space that was allocated to see how IPv6 fared in 2024.
Comparing 2023 to 2024, the number of individual allocations of IPv6 address space has increased by 1%, while the number of IPv4 allocation transactions has increased by 3% (Table 13).
| Allocations | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| IPv6 | 3,582 | 3,291 | 3,529 | 4,502 | 4,644 | 5,567 | 5,740 | 6,176 | 6,799 | 5,376 | 5,350 | 4,066 | 3,874 | 3,925 |
| IPv4 | 8,234 | 7,435 | 6,429 | 10,435 | 11,352 | 9,648 | 8,185 | 8,769 | 12,560 | 5,874 | 6,939 | 4,395 | 3,462 | 3,559 |
Table 13 — Number of individual address allocations, 2011 – 2024.
The amount of IPv6 address space distributed in 2024 is 60% less than the amount that was allocated in 2023, while the corresponding IPv4 volume has increased by 13% (Table 14).
| Addresses | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| IPv6 (/32s) | 14,986 | 17,710 | 23,642 | 17,847 | 15,765 | 25,260 | 19,975 | 38,699 | 35,924 | 21,620 | 28,131 | 27,497 | 74,159 | 45,015 |
| IPv4 (/32s)(M) | 191.7 | 88.8 | 57.7 | 58.8 | 32.3 | 20.8 | 15.1 | 14.1 | 13.9 | 4.2 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.8 |
Table 14 — Volume of address allocations, 2011 – 2024.
Regionally, each of the RIRs saw IPv6 allocation activity in 2024 that was on a par with those seen in 2023, but well short of the peak period of IPv6 allocation activity in 2018 to 2019 (Table 15).
| Allocations | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| AFRINIC | 129 | 82 | 72 | 59 | 81 | 111 | 110 | 108 | 111 | 108 | 135 | 151 | 115 | 117 |
| APNIC | 641 | 599 | 540 | 528 | 777 | 1,680 | 1,369 | 1,460 | 1,484 | 1,498 | 1,392 | 1,317 | 1,381 | 1,265 |
| ARIN | 1,035 | 603 | 543 | 489 | 604 | 645 | 684 | 648 | 601 | 644 | 668 | 680 | 712 | 951 |
| LACNIC | 130 | 251 | 223 | 1,199 | 1,053 | 1,007 | 1,547 | 1,439 | 1,614 | 1,801 | 725 | 635 | 612 | 656 |
| RIPENCC | 1,647 | 1,756 | 2,151 | 2,227 | 2,129 | 2,124 | 2,030 | 2,521 | 2,989 | 1,325 | 2,430 | 1,283 | 1,054 | 936 |
| Total | 3,582 | 3,291 | 3,529 | 4,502 | 4,644 | 5,567 | 5,740 | 6,176 | 6,799 | 5,376 | 5,350 | 4,066 | 3,874 | 3,925 |
Table 15 — IPv6 allocations by RIR.
The address assignment data tells a slightly different story. Table 16 shows the number of allocated IPv6 /32’s per year. The 2024 allocation IPv6 address volume in APNIC was extremely large, with the allocation of a /17 prefix (2410::) to Huawei International in November 2024 being the major part of the annual allocation volume.
| Addresses (/32s) | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| AFRINIC | 155 | 4,201 | 66 | 48 | 308 | 76 | 112 | 71 | 360 | 88 | 141 | 387 | 400 | 380 |
| APNIC | 9,506 | 3,807 | 4,462 | 2,663 | 2,108 | 1,235 | 4,228 | 19,681 | 7,945 | 7,365 | 10,185 | 4,856 | 599 | 33,257 |
| ARIN | 2,280 | 1,672 | 12,571 | 5,214 | 642 | 1,087 | 1,372 | 844 | 5,520 | 4,975 | 373 | 13,695 | 66,340 | 5,692 |
| LACNIC | 620 | 4,301 | 158 | 1,314 | 953 | 1,173 | 1,427 | 1,327 | 1,496 | 1,669 | 658 | 563 | 467 | 575 |
| RIPENCC | 2,425 | 3,729 | 6,385 | 8,608 | 11,754 | 21,689 | 12,836 | 16,776 | 20,603 | 7,523 | 16,774 | 7,996 | 6,353 | 5,111 |
| Total | 14,986 | 17,710 | 23,642 | 17,847 | 15,765 | 25,260 | 19,975 | 38,699 | 35,924 | 21,620 | 28,131 | 27,497 | 74,159 | 45,015 |
Table 16 — IPv6 address allocation volumes by RIR.
Dividing addresses by allocations gives the average IPv6 allocation size in each region (Table 17). Overall, the average IPv6 allocation size is a /28, with the RIPE NCC and ARIN averaging larger individual IPv6 allocations than the other RIRs.
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| AFRINIC | /31.7 | /26.3 | /32.1 | /32.3 | /30.1 | /32.5 | /32.0 | /32.6 | /30.3 | /32.3 | /31.9 | /30.6 | /30.2 | /30.3 |
| APNIC | /28.1 | /29.3 | /29.0 | /29.7 | /30.6 | /32.4 | /30.4 | /28.2 | /29.6 | /29.7 | /29.1 | /30.1 | /33.2 | /27.3 |
| ARIN | /30.9 | /30.5 | /27.5 | /28.6 | /31.9 | /31.2 | /31.0 | /31.6 | /28.8 | /29.1 | /32.8 | /27.7 | /25.5 | /29.4 |
| LACNIC | /29.7 | /27.9 | /32.5 | /31.9 | /32.1 | /31.8 | /32.1 | /32.1 | /32.1 | /32.1 | /32.1 | /32.2 | /32.4 | /32.2 |
| RIPENCC | /31.4 | /30.9 | /30.4 | /30.0 | /29.5 | /28.6 | /29.3 | /29.3 | /29.2 | /29.5 | /29.2 | /29.4 | /29.4 | /29.6 |
| Average | /29.9 | /29.6 | /29.3 | /30.0 | /30.2 | /29.8 | /30.2 | /29.4 | /29.6 | /30.0 | /29.6 | /29.2 | /27.7 | /28.5 |
Table 17 — Average IPv6 address allocation size by RIR.
The number and volume of IPv6 allocations per RIR per year is shown in Figures 14 and 15.
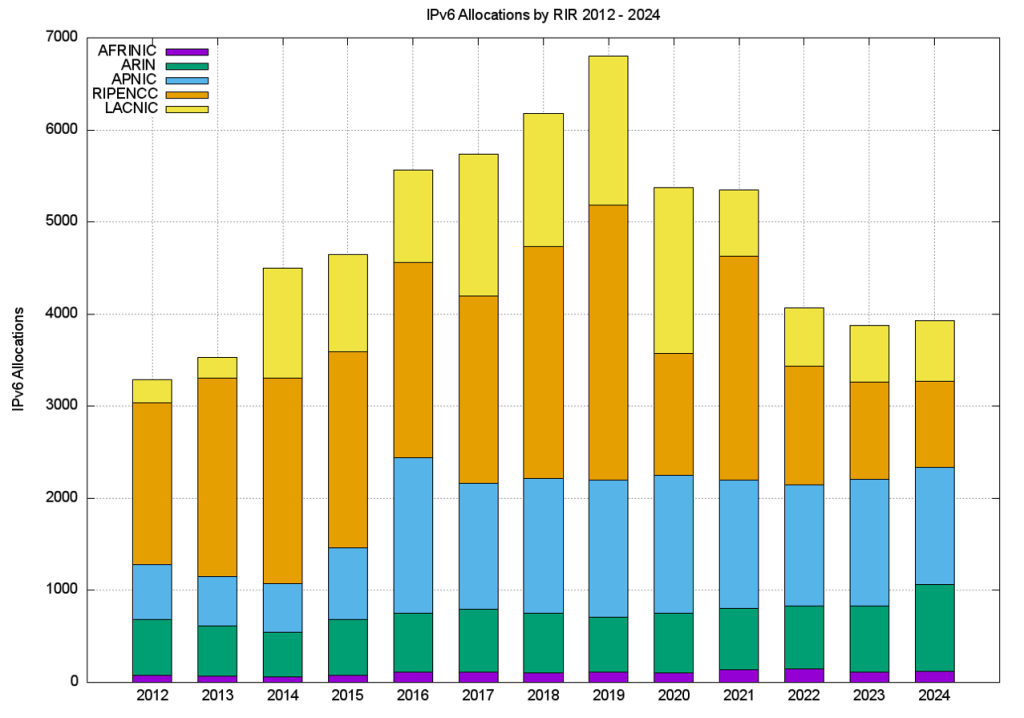
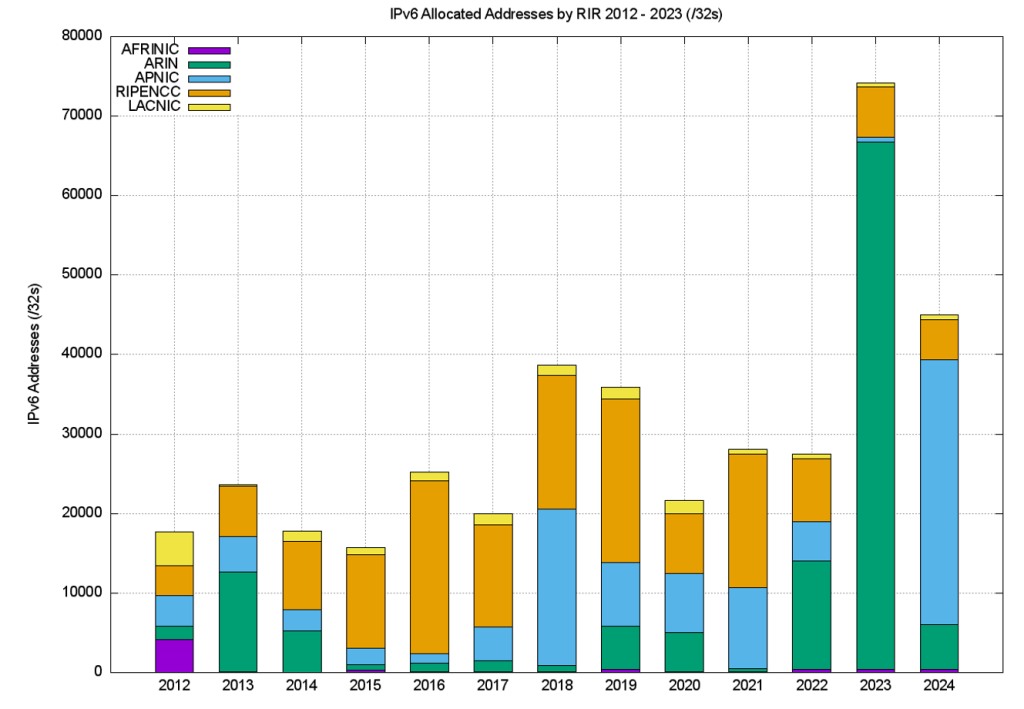
It might be tempting to ascribe the decline in 2020 of IPv6 allocations from the RIPE NCC to the year in which many European economies were hit hard by COVID-19 measures. Arguing against that is the observation that economies all over the world have been similarly affected, yet the decline in IPv6 allocation activity in 2020 is only seen in the data from the RIPE NCC. However, it’s an interesting question to ask as to why the IPv6 address allocation activity has slumped in the European economies (Tables 18 and 19).
| Rank | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | ||||||
| 1 | Brazil | 1,112 | Brazil | 1,394 | USA | 619 | USA | 638 | USA | 691 | USA | 889 |
| 2 | USA | 538 | USA | 588 | Russia | 576 | India | 377 | India | 424 | Brazil | 302 |
| 3 | Russia | 502 | Indonesia | 389 | Brazil | 508 | Brazil | 339 | Brazil | 267 | India | 269 |
| 4 | Germany | 407 | India | 226 | Netherlands | 448 | Bangladesh | 239 | Indonesia | 198 | Vietnam | 233 |
| 5 | Indonesia | 366 | Netherlands | 199 | India | 390 | Germany | 158 | Bangladesh | 159 | Indonesia | 169 |
| 6 | Netherlands | 342 | Germany | 192 | UK | 304 | Russia | 138 | Viet Nam | 143 | Bangladesh | 156 |
| 7 | UK | 223 | Bangladesh | 182 | Bangladesh | 213 | UK | 125 | Germany | 126 | Germany | 119 |
| 8 | Bangladesh | 202 | Russia | 128 | Germany | 196 | Indonesia | 113 | Colombia | 99 | Iran | 86 |
| 9 | France | 179 | Australia | 118 | Indonesia | 110 | Australia | 100 | Mexico | 96 | Australia | 83 |
| 10 | China | 165 | China | 115 | Hong Kong | 108 | Viet Nam | 91 | UK | 85 | Mexico | 83 |
Table 18 — IPv6 allocations by year and economy.
Table 18 shows the economies that received the largest number of individual IPv6 allocations, while Table 19 shows the amount of IPv6 address space assigned on a per economy basis for the past four years (using units of /32s).
| Rank | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | ||||||
| 1 | China | 6,787 | China | 6,765 | China | 5,424 | USA | 13,919 | USA | 66,579 | Singapore | 32,792 |
| 2 | USA | 5,510 | USA | 5,051 | Russia | 4,409 | China | 4,354 | Lithuania | 522 | USA | 5,533 |
| 3 | Russia | 3,716 | Brazil | 1,358 | India | 4,281 | Russia | 925 | UK | 513 | Iran | 643 |
| 4 | Germany | 2,522 | Netherlands | 1,331 | Netherlands | 3,390 | UK | 734 | Germany | 478 | Germany | 426 |
| 5 | Netherlands | 2,516 | Germany | 716 | UK | 2,249 | Germany | 706 | Russia | 371 | Lithuania | 410 |
| 6 | UK | 1,355 | Russia | 715 | Germany | 896 | Moldava | 456 | Ukraine | 369 | UK | 352 |
| 7 | France | 1,182 | UK | 552 | Ukraine | 651 | France | 404 | Iran | 314 | Turkey | 328 |
| 8 | Italy | 1,052 | Italy | 391 | Lithuania | 633 | Netherlands | 397 | France | 276 | South Africa | 304 |
| 9 | Brazil | 1,049 | France | 390 | Brazil | 502 | Italy | 363 | Seychelles | 258 | Canada | 292 |
| 10 | Spain | 854 | Turkey | 290 | USA | 491 | Brazil | 328 | Rwanda | 256 | Brazil | 289 |
Table 19 — IPv6 address allocation volumes by year and economy (/32s).
We can also look at the allocated address pools for the top 25 national economies (Table 20).
| Rank | CC | Allocated (/48s) | % Total | /48s per capita | Advertised /48s | Deployment | Name |
| 1 | US | 9,213,434,648 | 29.1% | 26.9 | 1,210,870,245 | 11.5% | USA |
| 2 | CN | 4,225,433,687 | 13.3% | 3.0 | 1,664,263,872 | 15.9% | China |
| 3 | SG | 2,257,203,689 | 7.1% | 371.7 | 9,445,725 | 0.1% | Singapore |
| 4 | DE | 1,585,120,019 | 5.0% | 19.0 | 1,054,733,850 | 10.1% | Germany |
| 5 | GB | 1,408,106,725 | 4.4% | 20.7 | 405,638,808 | 3.9% | UK |
| 6 | FR | 993,735,334 | 3.1% | 15.3 | 187,857,414 | 1.8% | France |
| 7 | RU | 727,187,782 | 2.3% | 5.1 | 244,298,888 | 2.3% | Russia |
| 8 | NL | 714,342,719 | 2.3% | 40.4 | 341,924,543 | 3.3% | Netherlands |
| 9 | IT | 698,748,971 | 2.2% | 11.9 | 436,310,346 | 4.2% | Italy |
| 10 | JP | 669,589,718 | 2.1% | 5.5 | 512,858,598 | 4.9% | Japan |
| 11 | AU | 621,872,441 | 2.0% | 23.2 | 310,137,856 | 3.0% | Australia |
| 12 | BR | 547,850,208 | 1.7% | 2.5 | 427,490,414 | 4.1% | Brazil |
| 13 | SE | 458,293,609 | 1.4% | 42.8 | 90,703,579 | 0.9% | Sweden |
| 14 | IN | 441,714,156 | 1.4% | 0.3 | 373,461,523 | 3.6% | India |
| 15 | PL | 407,306,495 | 1.3% | 10.2 | 234,560,448 | 2.2% | Poland |
| 16 | ES | 405,405,742 | 1.3% | 8.5 | 112,156,049 | 1.1% | Spain |
| 17 | SC | 374,145,029 | 1.2% | 3446.3 | 124,140,536 | 1.2% | Seychelles |
| 18 | ZA | 349,639,870 | 1.1% | 5.7 | 317,857,002 | 3.0% | South Africa |
| 19 | KR | 345,833,482 | 1.1% | 6.7 | 2,559,149 | 0.0% | Korea |
| 20 | AR | 345,639,028 | 1.1% | 7.5 | 286,387,153 | 2.7% | Argentina |
| 21 | TR | 273,940,512 | 0.9% | 3.2 | 55,964,935 | 0.5% | Turkey |
| 22 | EG | 271,384,581 | 0.9% | 2.4 | 270,925,826 | 2.6% | Egypt |
| 23 | AE | 265,617,419 | 0.8% | 27.6 | 215,351,617 | 2.1% | UAE |
| 24 | CH | 263,586,240 | 0.8% | 29.7 | 122,323,090 | 1.2% | Switzerland |
| 25 | IR | 248,315,915 | 0.8% | 2.8 | 55,300,289 | 0.5% | Iran |
Table 20 — IPv6 allocated address pools per national economy, December 2024.
While the United States tops this list of the total pool of allocated IPv6 addresses with 31% of the total span of allocated IPv6 addresses, the per capita number is lower than others in this list (Netherlands, Sweden, Switzerland). In 2023 ARIN allocated a /16 address block to Capital One Financial Cooperation, one of the larger banks in the United States with a large credit card base in retail operations. In 2024, APNIC allocated a /17 to Huawei International, with a corporate location in Singapore.
Twenty years ago, it was common practice to point out the inequities in the state of IPv4 address deployment. At the time, some US universities had more IPv4 addresses at their disposal than some highly populated developing economies, and the disparity was a part of the criticism of the address management practices that were used at the time. The RIR system was intended to address this issue of predisposition to a biased outcome.
The concept behind the system is that within the regional community each community had the ability to develop their own address distribution policies and could determine for themselves what they meant by such terms as ‘fairness’ and ‘equity’ and then direct their regional address registry to implement these policies. While IPv4 had a very evident early adopter reward, in that the address allocations in the IPv4 class-based address plan could be quite extravagant, the idea was that in IPv6, where the address allocations were developed from the outset through local bottom-up policy determinate frameworks, such evident inequities in the outcome would be avoided, or so it was hoped.
It was also envisaged that with such a vast address plan provided by 128 bits of address space, the entire concept of scarcity and inequity would be largely irrelevant. 2128 is a vast number and the entire concept of comparison between two vast pools of addresses is somewhat irrelevant. So, when we look at the metric of /48s per head of population, don’t forget that a /48 is actually 80 bits of address space, which is massively larger than the entire IPv4 address space. Even India’s average of 0.3 /48s per capita is still a truly massive number of IPv6 addresses!
However, before we go too far down this path it is also useful to bear in mind that the 128 bits of address space in IPv6 has become largely a myth. We sliced off 64 bits in the address plan for no particularly good reason, as it turns out. We then sliced off a further 16 bits for again no particularly good reason. 16 bits for end site addresses allows for 65,000 distinct networks within each site, which is somewhat outlandish in pretty much every case.
The result is that the vastness of the address space represented by 128 bits in IPv6 is, in fact, not so vast in practice. The usable address prefix space in IPv4 roughly equates to a /32 end address in IPv4 with around a /48 prefix in IPv6. So perhaps this comparison of /48s per capita is not entirely fanciful, and there is some substance to the observation that there are inequities in the address distribution in IPv6 so far. However, unlike IPv4, the exhaustion of the IPv6 address space is still quite some time off, and we still believe that there are sufficient IPv6 addresses to support a uniform address use model across the entire world of silicon over time.
There is a larger question about the underlying networking paradigm in today’s public network. IPv6 attempts to restore the 1980s networking paradigm of a true peer-to-peer network where every connected device can send packets to any other connected device. However, today’s networked environment regards such unconstrained connectivity as a liability.
Exposing an end client device is regarded as being unnecessarily foolhardy, and today’s network paradigm relies on client-initiated transactions. This is well-suited to NAT-based IPv4 connectivity, and the question regarding the long-term future of an IPv6 Internet is whether we want to bear the costs of maintaining end-client unique addressing plans, or whether NATs in IPv6 might prove to be a most cost-effective service platform for the client side of client/server networks.
To what extent are allocated IPv6 addresses visible as advertised prefixes in the Internet’s routing table?
Figure 16 shows the overall counts of advertised, unadvertised and total allocated address volume for IPv6 since 2010, while Figure 16 shows the advertised address span as a percentage of the total span of allocated and assigned IPv6 addresses.
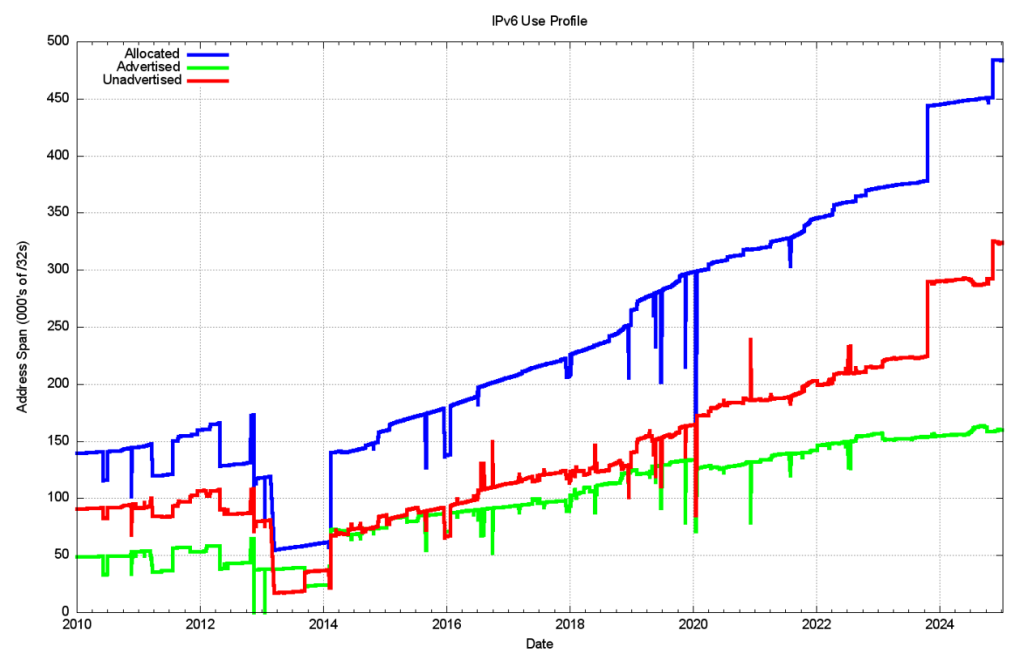
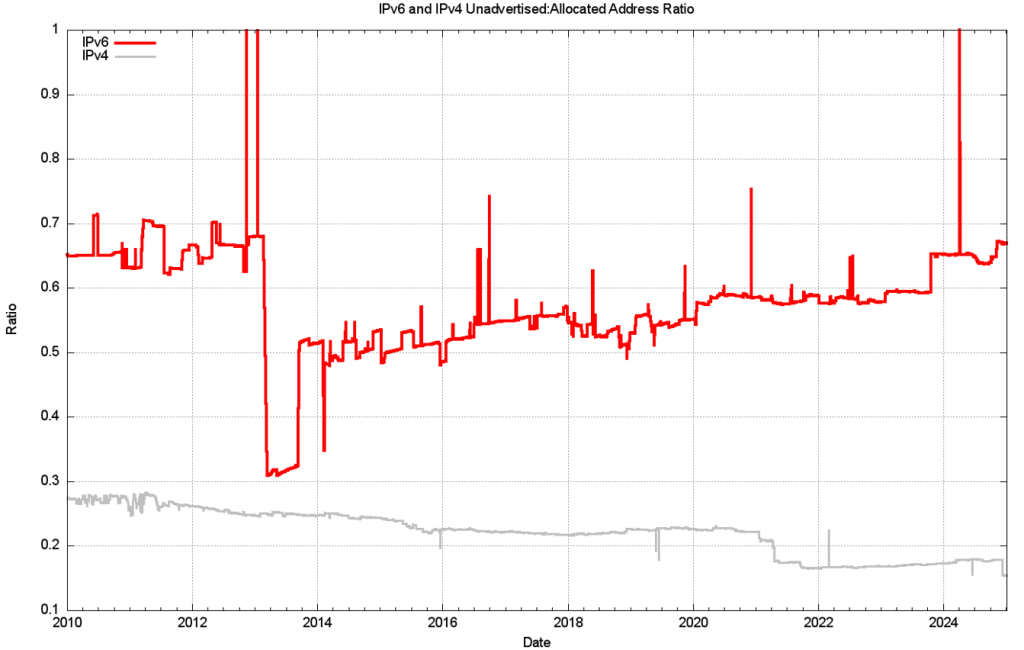
The drop in the allocated address span in 2013 is the result of a change in LACNIC where a single large allocation into Brazil was replaced by the recording of direct allocation and assignments to ISPs and similar end entities.
From a history of careful conservation of IPv4 addresses, where 85% of allocated or assigned IPv4 addresses are advertised in the BGP routing table, a comparable IPv6 figure of 34% does not look all that impressive. But that’s not the point. We chose the 128-bit address size in IPv6 to allow addresses to be used without overriding concerns about conservation. We’re allowed to be inefficient in address use in IPv6!
At the start of 2025, we’ve advertised an IPv6 address span that is the equivalent of 160,000 /32s, or 10.5B end-site /48 prefixes. That is just 0.0037% of the total number of /48 prefixes in IPv6.
The outlook for the Internet
Once more the set of uncertainties that surround the immediate future of the Internet are considerably greater than the set of predictions that we can be reasonably certain about.
The year 2017 saw a sharp rise in IPv6 deployment, influenced to a major extent by the deployment of IPv6 services in India, notably by the Reliance Jio mobile service. The next year, 2018, was a quieter year, although the rise in the second half of the year is due to the initial efforts of mass-scale IPv6 deployment by some major Chinese service providers. This movement accelerated in 2019 and the overall move of a further 5% in IPv6 deployment levels had a lot to do with the very rapid rise of the deployment of IPv6 in China. There has been an ongoing rise in the level of IPv6 within China, and the measured level of IPv6 has risen from 32% of the user base to 42% over 2024, or an expansion of the Chinese IPv6 user pool by 80M end clients over the year.
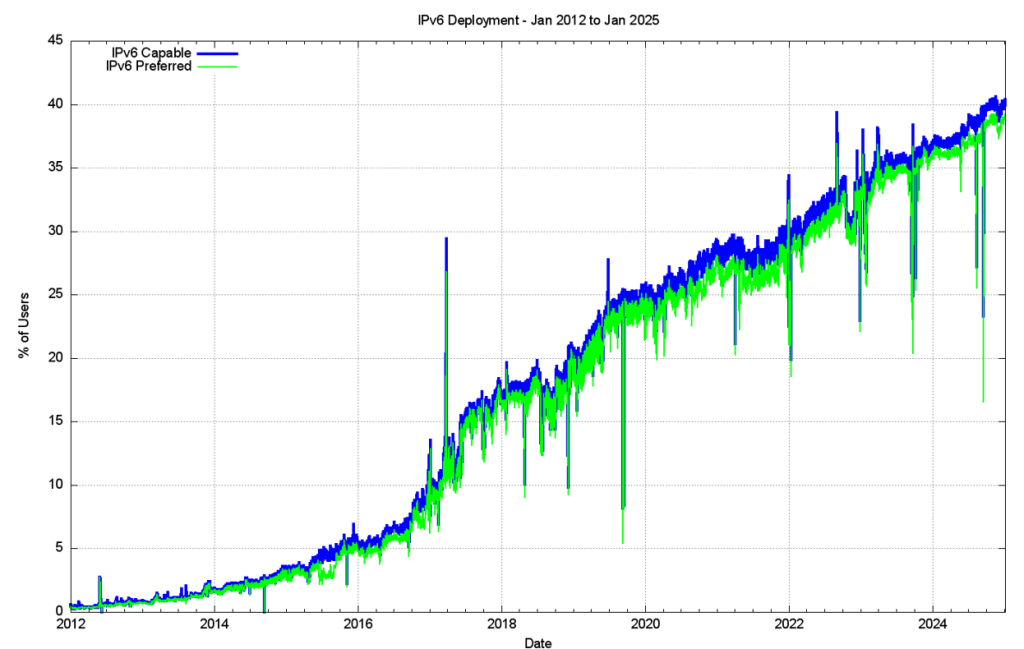
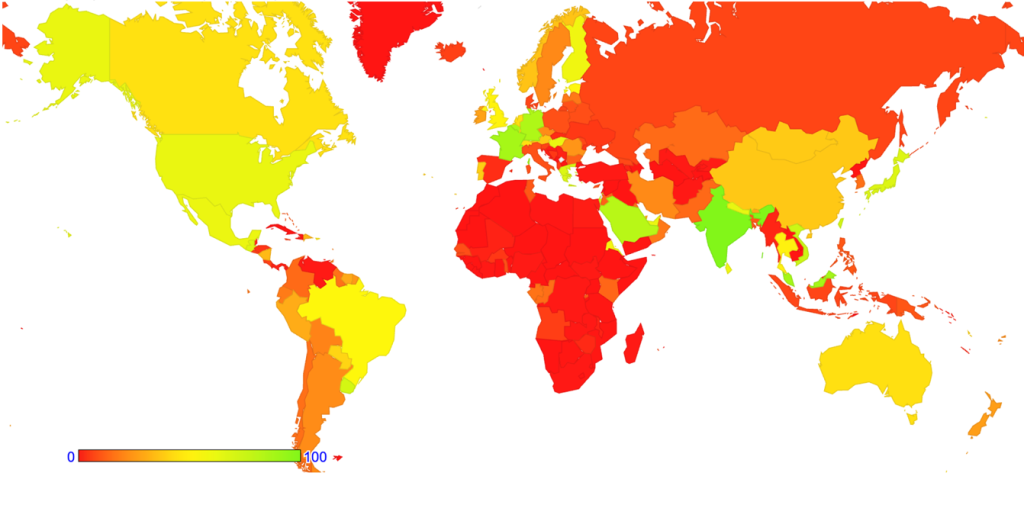
In 2024, the growth patterns for IPv6 are more diffuse around the world with a 3.7% overall growth rate, although there has been steady growth in IPv6 deployment in Mongolia (42%), Bhutan (34%) and Nepal (55%) (Figure 19).
While a number of service operators have reached the decision point that the anticipated future costs of NAT deployment are unsustainable for their service platform, there remains a considerable school of thought that says that NATs will cost-effectively absorb some further years of Internet population growth. At least that’s the only rationale I can ascribe to a very large number of service providers who are making no visible moves to deploy dual-stack services now. Given that the ultimate objective of this transition is not to turn on dual-stack everywhere, but to turn off IPv4, there is still some time to go, and the uncertainty lies in trying to quantify what that time might be.
The period of the past decade has been dominated by the mass marketing of mobile Internet services, and the Internet’s growth rates for 2014 through to 2016 perhaps might have been the highest so far recorded. This would’ve been visible in the IP address deployment data were it not for the exhaustion of the IPv4 address pool. In address terms this growth in the IPv4 Internet is being almost completely masked by the use of Carrier Grade NATs in the mobile service provider environment so that the resultant demands for public addresses in IPv4 are quite low and the real underlying growth rates in the network are occluded by these NATs. In IPv6, the extremely large size of the address space masks out much of this volume. A single IPv6 /20 allocation to an ISP allows for 268M /48 allocations, or 68B/56 allocations, so much of the growth in IPv6-using networks is simply hidden behind the massive address plan that lies behind IPv6.
It has also been assumed that we should see IPv6 address demands for deployments of large-scale sensor networks and other forms of deployments that are encompassed under the broad umbrella of the Internet of Things (IoT). This does not necessarily imply that the deployment is merely a product of an over-hyped industry, although that is always a possibility. It is more likely to assume that, so far, such deployments are taking place using private IPv4 addresses, and they rely on NATs and application-level gateways to interface to the public network. Time and time again we are lectured that NATs are not a good security device, but in practice, NATs offer a reasonable front-line defence against network scanning malware, so there may be a larger story behind the use of NATs and device-based networks than just a simple conservative preference to continue to use an IPv4 protocol stack.
More generally, we are witnessing an industry that is no longer using technical innovation, openness and diversification as its primary means of expansion. The widespread use of NATs in IPv4 limits the technical substrate of the Internet to a very restricted model of simple client/server interactions using TCP and UDP. The use of NATs forces the interactions into client-initiated transactions, and the model of an open network with considerable flexibility in the way in which communications take place is no longer being sustained in today’s network. Incumbents are entrenching their position and innovation and entrepreneurialism are taking a back seat while we sit out this protracted IPv4/IPv6 transition.
What is happening is that today’s Internet carriage service is provided by an ever-smaller number of very large players, each of whom appears to be assuming a very strong position within their respective markets. The drivers for such larger players tend towards risk aversion, conservatism and increased levels of control across their scope of operation. The same trends of market aggregation are now appearing in content provision platforms, where a small number of platform operators are exerting a completely dominant position across the entire Internet.
The evolving makeup of the Internet industry has quite profound implications in terms of network neutrality, the separation of functions of carriage and service provision, investment profiles and expectations of risk and returns on infrastructure investments, and on the openness of the Internet itself. Given the economies of volume in this industry, it was always going to be challenging to sustain an efficient, fully open, and competitive industry that was capable of sustaining both large and small operators, but the degree of challenge in this agenda is multiplied many-fold when the underlying platform has run out of the basic currency of IP addresses. The pressures on the larger players within these markets to leverage their incumbency into overarching control gains traction when the stream of new entrants with competitive offerings dries up, and the solutions in such scenarios typically involve some form of public sector intervention directed to restore effective competition and revive the impetus for more efficient and effective offerings in the market.
As the Internet continues to evolve, it is no longer the technically innovative challenger pitted against venerable incumbents in the forms of the traditional industries of telephony, print newspapers, television entertainment and social interaction. The Internet is now the established norm. The days when the Internet was touted as a poster child of disruption in a deregulated space are long since over, and these days we appear to be increasingly looking further afield for a regulatory and governance framework that can challenge the increasing complacency of the very small number of massive digital incumbents.
It is unclear how successful we will be in this search for responses to this oppressive level of centrality in many aspects of the digital environment. We can but wait and see.
The views expressed by the authors of this blog are their own and do not necessarily reflect the views of APNIC. Please note a Code of Conduct applies to this blog.

I personally believe that IPv6 will soon see an accelerated growth in adoption.
Many large CDN’s and platforms have moved towards IPv6 behind the scenes.
And reaching 50% IPv6 availability would probably be an argument that would convince many to adopt it.
And new ISP’s would likely be IPv6-mostly, given the fact that new v4 blocks cost a lot.
Africa is also getting more infrastructure in place, and they will most likely have IPv6 in place as a cheaper alternative.
(Yes, not adopting IPv6 is indirectly hurting developing nations.)
There are still some issues with it though.
For example, take the v6-only website http://clintonwhitehouse2.archives.gov/ .
Browsers on an IPv4-only network will show an error page that is basically saying that this website does not exist.
This is the exact same error page as for doesnotexist.example.com, which as it’s name suggests, does actually not exist.
(Chrome bug: https://issues.chromium.org/issues/40736240 , related bugs are linked in someones comment.)
And some websites that test a connection also don’t do much regarding IPv6, while they should probably be the first ones to support it properly.
For example, those “is it down” tools that check whether a website is online more often than not fail to do their job at the above-mentioned archive.
(And speed tests should ideally check for both v4 and v6 connectivity, but that’s my personal opinion.)
2024 is over.
Lets see what happens to IPv6 in 2025!