
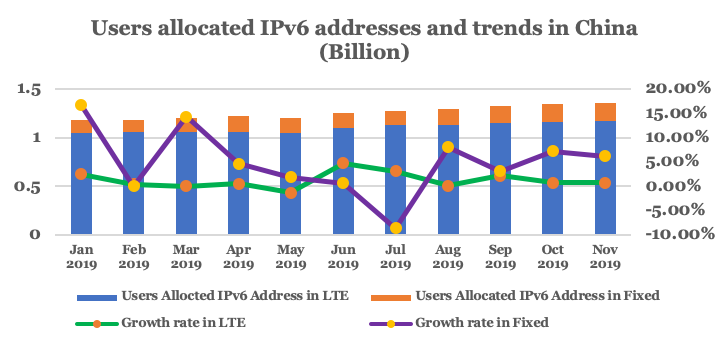
Since the release of the government’s IPv6 Action Plan in 2017, IPv6 deployment in China has made steady gains, especially among LTE networks. By the end of 2019, more than 90% (~1.2 billion) of LTE users in China have been allocated IPv6 addresses.
In response, many well-known applications in China, such as Taobao, Alipay, Youku, Tencent Video, Baidu maps, and Weibo, now support IPv6. This has resulted in a considerable increase in active IPv6 users over the past six months (Figure 1).
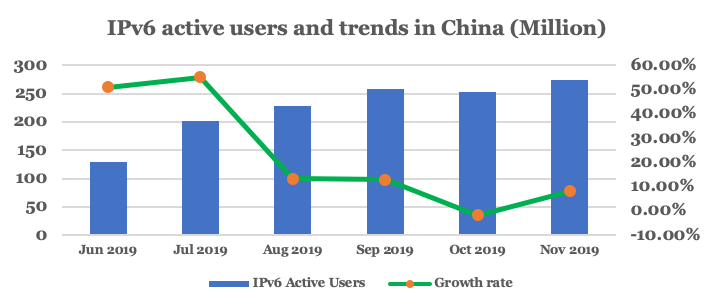
Although the transformation of fixed networks has been slower, the numbers are still relatively good: 45% (189,000,000) of fixed network users have been allocated IPv6 addresses. According to sampling, less than 42% of fixed terminals can currently support IPv6, therefore, the replacement of these fixed terminals requires urgent work.
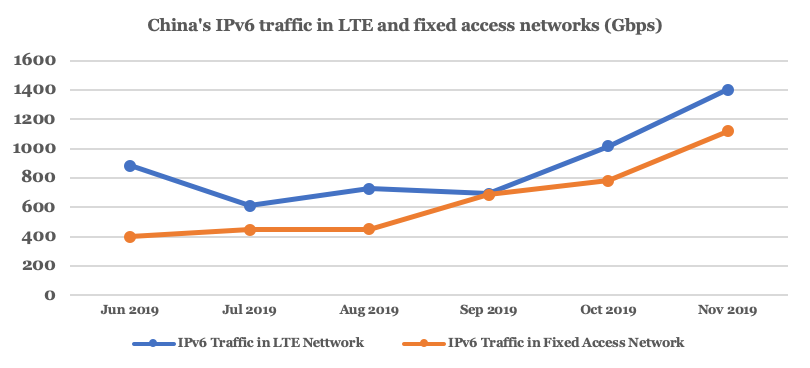
IPv6 traffic is another key indicator of the level of IPv6 development.
By November 2019, IPv6 traffic over the LTE core network in China had reached 1.399Tbps, a 129% increase from July 2019. Traffic over the fixed network was not far behind, thanks to a significant increase in the past six months (Figure 3).
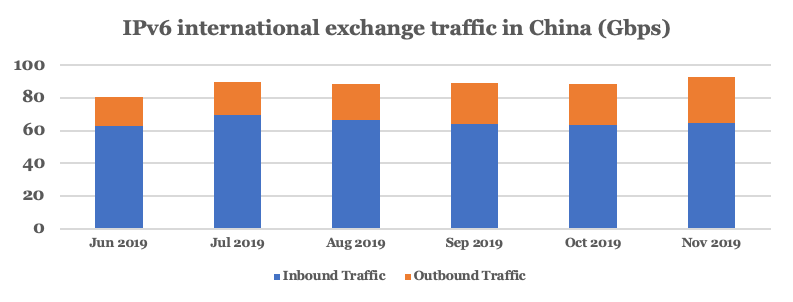
Connectivity between different carriers has also grown rapidly, from 16.46Gbps at the beginning of 2019 to 200.72Gbps, and the performance of the inter-networking between different carriers is also growing.
Looking at international exchange traffic, total traffic grew by almost 15% in the past six months, reaching more than 92Gbps in November 2019. Of this, inbound traffic is more than double that of outbound (Figure 4); the significant difference between these two demonstrates the need to improve IPv6 application resources in China.
Network infrastructure
While IPv6 has been deployed by some in China since 2012, it hasn’t been until recently that it has become the ‘standard’ across the whole network infrastructure, with a preference towards dual-stack.
2018 — All backbone networks and LTE core networks completed IPv6 upgrades and started to provide services to users.
2019 — All Internet backbone IXPs supported IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack.
2019 — All metropolitan networks and fixed access networks completed IPv6 upgrades.
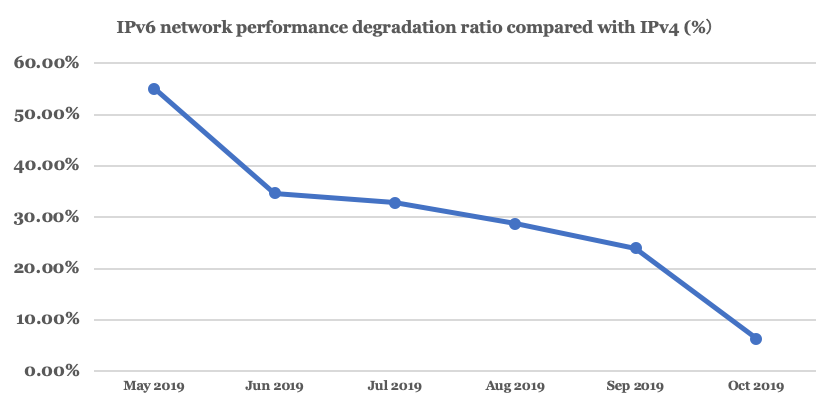
The Action Plan has played a role in this uptick, so too has the improvement in IPv6 network performance, which is now close to that of IPv4 (Figure 5).
Content infrastructure
Given that a vast majority of Internet content accessed in China is hosted locally, much effort has been spent to encourage organizations managing local content infrastructure, including data centres (IDCs), content delivery networks (CDNs), cloud services and the DNS, to deploy IPv6. As can be seen from the following reports from the end of 2019, these efforts have been rewarded:
- More than 1,000 IDCs support IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack
- 60% of CDN nodes are IPv6-enabled
- The top 10 cloud service providers, including Aliyun, Tencent Cloud and Huawei Cloud, have upgraded 12 typical cloud services, such as ECS, SLB, WAF and Database, to support IPv6, and have been able to provide users with basic IPv6 services
- The recursive domain name servers run by ISPs are fully supporting IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack
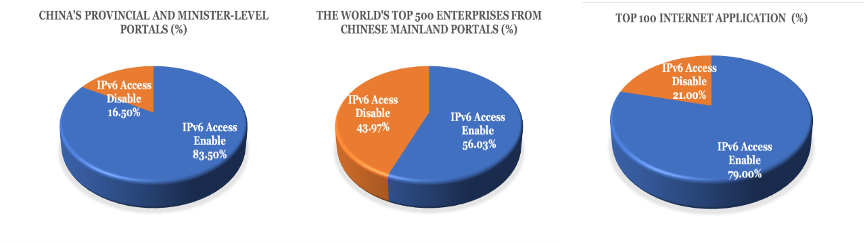
Leading by example, the government has upgraded the majority of its websites and applications to be IPv6 capable — by the end of 2018, 83.5% of China’s provincial and minister-level portals supported IPv6 access.
Enterprises have followed suit with 56% of the world’s top 500 enterprises from the Chinese mainland (totalling 116 enterprises) and 79% of the top 100 Internet sites and applications supporting IPv6 access (as of Nov 2019).
Resourcing the growing supply for IPv6
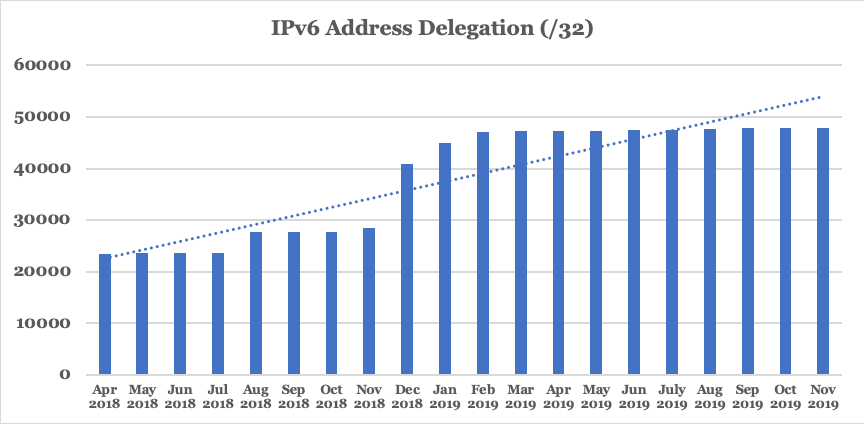
As of November 2019, the number of IPv6 address delegations in China had reached 47,851 (/32s) (Figure 7).
This amount is meeting China’s current IPv6 requirements, however, with the rapid development of Internet of Things, Internet of Vehicles and the Industrial Internet, it is expected that demand will increase further in the future.
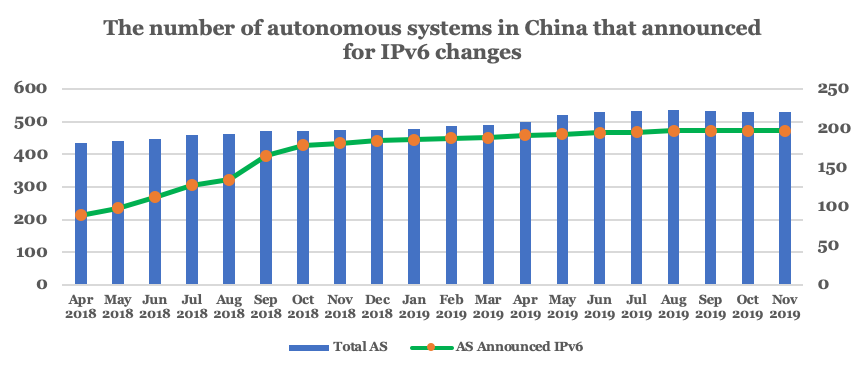
It is also great to see that more than one in three Autonomous Systems (ASes) in China have announced IPv6 (Figure 8).
More success to come
In its first two years, China’s IPv6 deployment Action Plan has greatly improved IPv6 deployment and usage, with active users now exceeding 270 million, IPv6 traffic exceeding 1Tb, and 90% of the network infrastructure supporting IPv6. We are looking forward to seeing these gains continue in 2020 and beyond.
This article is a summary of The Development of IPv6 in China Report produced by the Committee of Experts on Advancing IPv6 Scale Deployment in China, December 2019.
Ke Ma is a senior network engineer in the Committee of Experts on Advancing IPv6 Scale Deployment in China, responsible for the construction of the China IPv6 development monitoring platform.
The views expressed by the authors of this blog are their own and do not necessarily reflect the views of APNIC. Please note a Code of Conduct applies to this blog.
